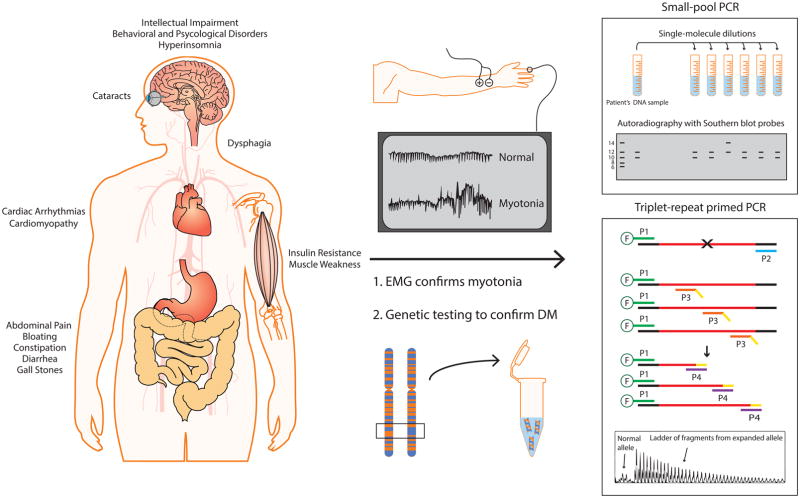
Figure 1. Schematic of genetic testing used to diagnose DM.
DM is a multisystemic disorder that primarily affects skeletal muscle, heart, brain, eyes, CNS, and GI tract. Electromyography (EMG) is used to assess myotonia in suspected individuals. Genetic testing is performed using the patient’s DNA sample, typically from the blood. There are two distinct laboratory procedures for genetic testing: SP-PCR and TP-PCR. SP-PCR requires single-molecule dilutions of extracted DNA, which are individually PCR amplified and probed with Southern blot hybridization. This method readily amplifies repeats from individual molecules, avoiding the amplification bias for the smaller allele commonly observed in conventional PCR. Similarly, TP-PCR is an improved method for detecting larger repeats. During the early amplification cycles, 5′ fluorescently labeled primer P1 and repeat specific primer P3 with 5′ tail sequence (in yellow) generate multiple products. The primer P4, which shares the 5′ tail sequence, subsequently amplifies the products from the previous amplification cycles. A 10:1 ratio of P4 to P3 ensures that P3 is exhausted in the early amplification cycles. Flanking and repeat DNA are shown in black and red, respectively.