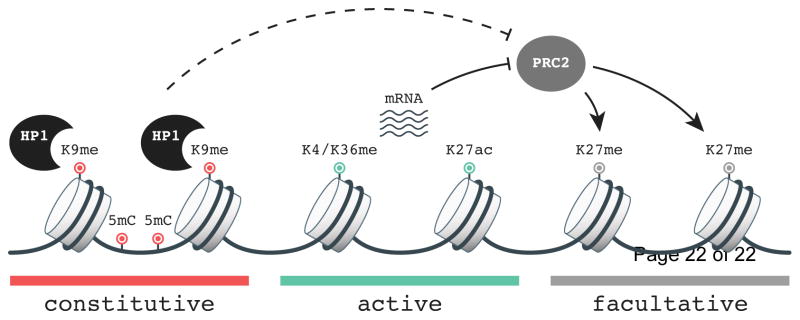
Figure 1. Model in which PRC2 responds to the chromatin environment to establish H3K27me domains.
Repressive features of constitutive heterochromatin including DNA methylation (5mC), H3K9me (K9me), and HP1 binding influence methylation of H3K27 by PRC2. Conversely, histone modifications associated with transcription such as H3K4me (K4me), H3K36me (K36me), and H3K27ac (K27ac), as well as RNA can directly inhibit PRC2 catalytic activity to prevent H3K27me at regions of active gene expression. Genomic regions that do not contain features of active or repressed chromatin may be targeted by PRC2. Other properties of the chromatin environment such as nucleosome occupancy, chromosome conformation and location within the nucleus (not pictured) may also contribute to PRC2 target selection.