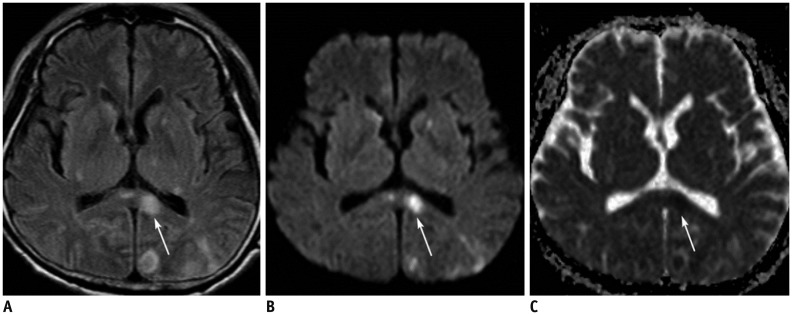
Fig. 5. 62-year-old male patient with acute splenial infarction.
A, B. Axial FLAIR image (A) and DWI (B) show multiple hyperintense lesions in bilateral basal ganglia, left thalamus, splenium of corpus callosum (arrows), and left occipital lobe. Splenial lesion (arrows) is more conspicuously demonstrated on DWI than on FLAIR image. C. ADC map image reveals restricted water diffusion of lesion (arrow). ADC = apparent diffusion coeffcient, DWI = diffusion-weighted image, FLAIR = fluid-attenuated inversion recovery