Figure 8.
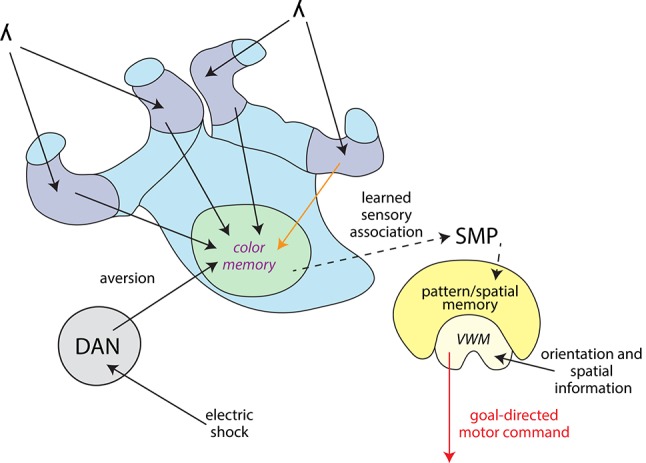
Information flow model for differential color learning in a binary choice assay. Information about the light wavelength (λ) enters the collar region (dark blue) of the MBC from the optic neuropils. Visual information is passed on from the collar region to the VL (light green) via Kenyon cells. This process was partially disrupted by a procaine injection into one collar region (orange arrow). Electric shock information is passed on from the ventral nerve cord to dopaminergic neurons (DAN, gray) which modulate MB output. In the VL wavelength information is associated with aversion and most likely color memories are formed here. This process was disrupted by procaine-injections into the VL (marked in purple). Information about the learned sensory association might be passed on indirectly to the CX (yellow) via the superior medial protocerebrum (SMP). The CX receives orientation and spatial information and processes how the animal is orientated in relation to its environment using visual working memory (VWM). The CX initiates a goal-directed motor response, possibly modified in regards to the learned sensory association. This process was disrupted by procaine-injections into the CX (red arrow).
