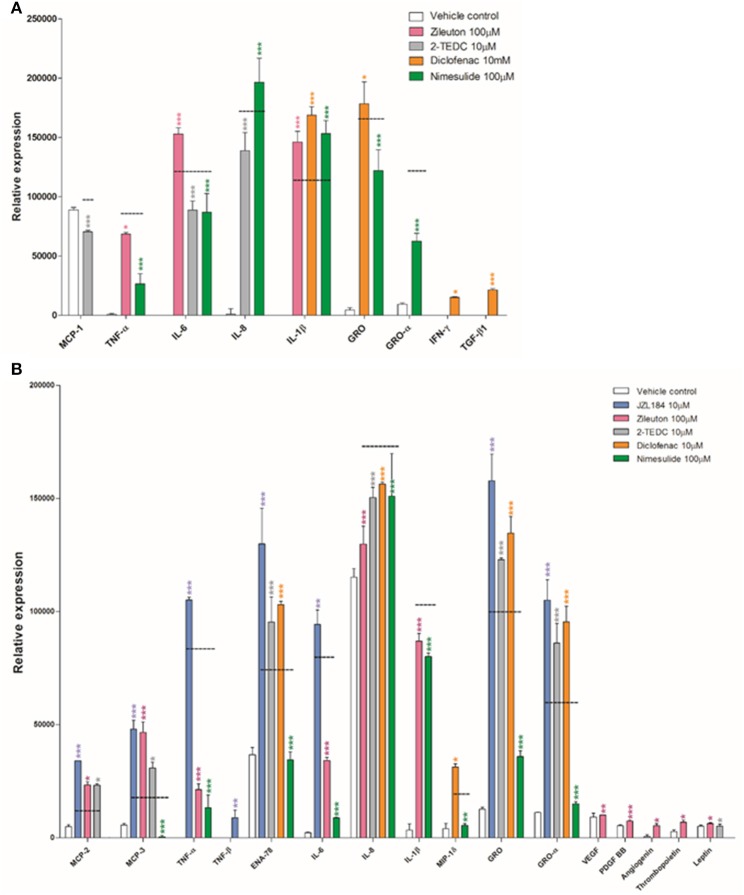
Figure 2.
(A) Human fetal astrocytes exposed to TNF-α and IL-1β (50 ng/ml), were incubated with the 5, -12, and -15 LOX inhibitor 2-TEDC (gray) which reduced significantly the secretion of MCP-1, IL-6 and IL-8 (p < 0.001); the COX-2 inhibitor, nimesulide (green) reduced significantly the secretion of TNF-α, IL-6, GRO and GRO-α (p < 0.001) but at the same time increased the secretion of IL-1β and IL-8 (p < 0.001), when compared to astrocytes not exposed to inhibitors (black dashed line). The COX-1/COX-2-inhibitor, diclofenac (orange) increased the levels of IL-1β, TGF-β (p < 0.001), GRO and IFN-γ (p < 0.05) when compared to astrocytes not exposed to inhibitors. (B) In human fetal microglia exposed to TNF-α and IL-1β, the COX-2 inhibitor, nimesulide reduced significantly the secretion of MCP-3, TNF-α, ENA-78, IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, GRO, and GRO-α (p < 0.001), MCP-2 and MIP-1δ (p < 0.01) and the 5-LOX inhibitor, zileuton (pink) reduced significantly the secretion of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-1β (p < 0.001), in comparison to microglia not exposed to inhibitors. n = 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.