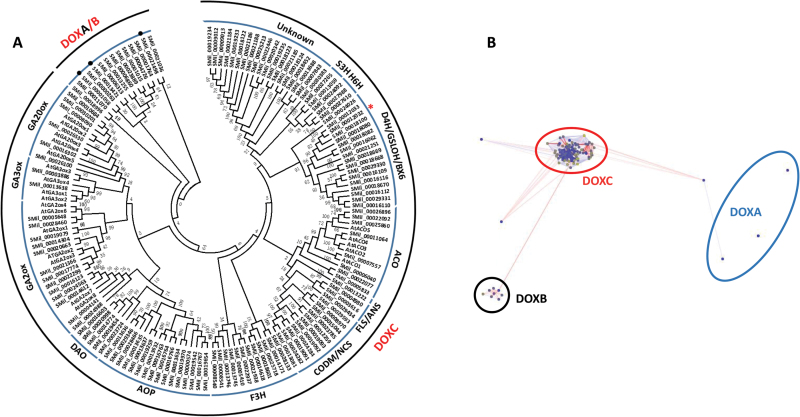
Fig. 1.
(A) Analysis of the phylogenetic relationships of 2OGD gene members in S. miltiorrhiza. A total of 132 2OGD proteins from S. miltiorrhiza were used to construct a neighbor-joining tree. Bootstrap values are presented for all branches. The 132 2OGDs were clustered into two classes, and then the DOXC class was divided into 11 clades. These clades were named according to their known functions in other species. The asterisk (*) indicates 2OGD5, on which functional analysis was performed. (B) The CLANS analysis clustered the 2OGDs into three classes (DOXA, DOXB, and DOXC). Three 2OGD members were classified into the DOXA class, which differed from the phylogenetic tree. Connected dots indicate significant similarity (P<10–4) based on the BLASTP search. The other three dots outside of the DOXA–C clusters were clustered in the unclassified group.