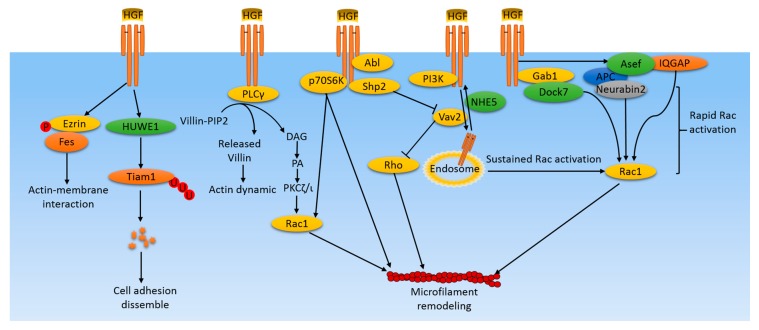
Figure 1.
Microfilament-related pathways induced by HGF/cMet in cancer cells. HGF/cMet activates various pathways in cancer cells leading to microfilament remodeling, which plays an important role in cell lamellipodium formation, protrusion, migration, and metastasis. HGF induces rapid Rac activation by activating the Rac1 upstream regulator, GEF, for example, Asef and IQGAP. Simultaneously, Rac activity is maintained by distinct mechanisms involving the cMet receptor containing endosome translocations to the perinuclear area and to the cell membrane. In addition, some kinases and phosphatases are activated by HGF, leading to microfilament remodeling through the Rac/Rho system or through the direct interactions with actin filaments. Some supplemental mechanisms include ubiquitylization of signaling molecules, like Tiam, leading to perturbations of its downstream effectors, and phosphorylation of Ezrin, which mediates interactions between actin filaments and the cell membrane.