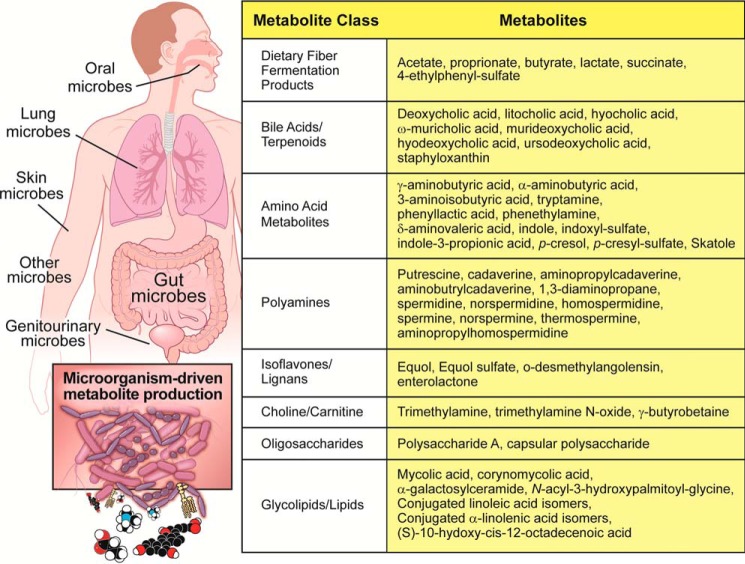
Figure 1.
Small molecule metabolites originating from the human microbiome. Diverse bacterial ecosystems present in the oral cavity, upper and lower gastrointestinal tract, skin surface, lungs, and almost every exposed orifice studied possess the enzymatic machinery to generate chemically diverse and biologically active metabolites that impact host health and disease. Collectively, human microbiota represent a major contributor to the chemical diversity in the human metaorganism, and many known bacterial metabolites have dedicated host receptor systems that allow for microbe-host cross-talk that modulates human health and disease.