Figure 1.
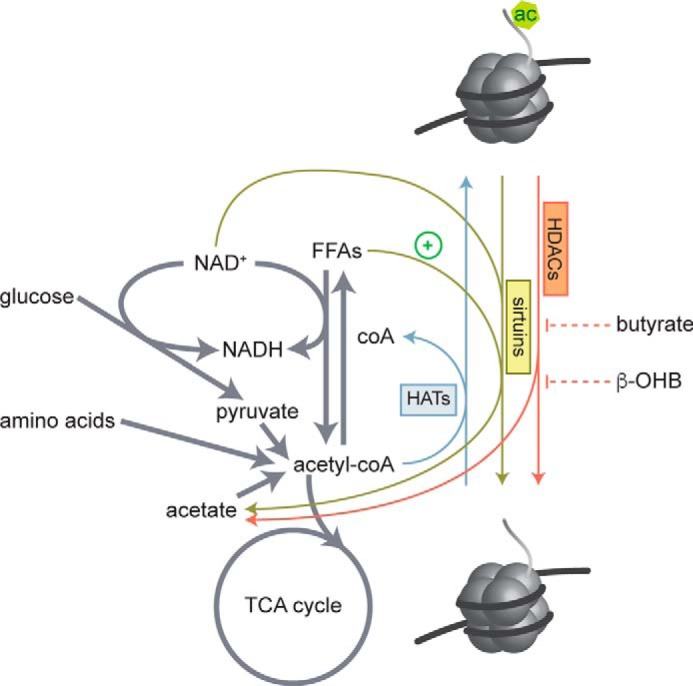
Regulation of histone acetylation by metabolites. HAT enzymes use acetyl-CoA as a necessary co-substrate for histone acetylation and produce CoA. Acetyl-CoA pools are fed by oxidation of free fatty acids (FFAs), glucose, and degradation of amino acids. HDAC enzymes hydrolyze acetyl groups from histone lysine residues and produce acetate. The class III HDACs, sirtuins, require NAD+ as a necessary co-substrate and produce NADH and acetate. Sirt6 is also activated by long chain free fatty acids. Class I, IIa, IIb, and IV sirtuins do not require NAD+ but are inhibited by butyrate and the ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate (β-OHB).
