Figure 10.
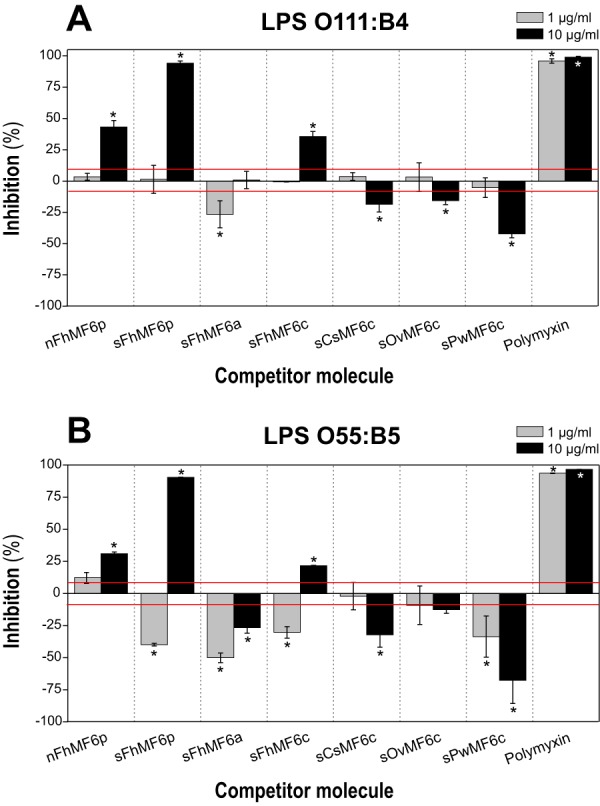
Competitive displacement of LPS binding to PMX. Samples of FITC-LPS from E. coli serotypes O111:B4 (A) and O55:B5 (B) were preincubated at concentrations of 1.25 and 2.5 μg/ml, respectively, in PBS-EDTA-BSA with 10 and 1 μg/ml concentrations of the following proteins/peptides: whole native (nFhMF6p) and synthetic (sFhMF6p); the N- (sFhMF6a) and C-terminal (sFhMF6c) regions of Fasciola MF6p/FhHDM-1; the C-terminal region of orthologous proteins sCsMF6c, sOvMF6c, and sPwMF6c; and PMX. A 100-μl volume of each sample was then added to the wells containing biotinylated PMX captured by deglycosylated avidin. The results are expressed as percentage of inhibition of LPS binding to PMX by the target protein/peptide and are the mean values ±S.D. (error bars) for duplicate wells. The average A (492 nm) obtained for control wells (without inhibitor) was 1.06 ± 0.09 and 0.81 ± 0.05 for serotypes O111:B4 and O55:B5, respectively. The red line indicates the ±S.D. percentage values of control wells. Differences in bars marked with an asterisk were significant at p < 0.05.
