Figure 6.
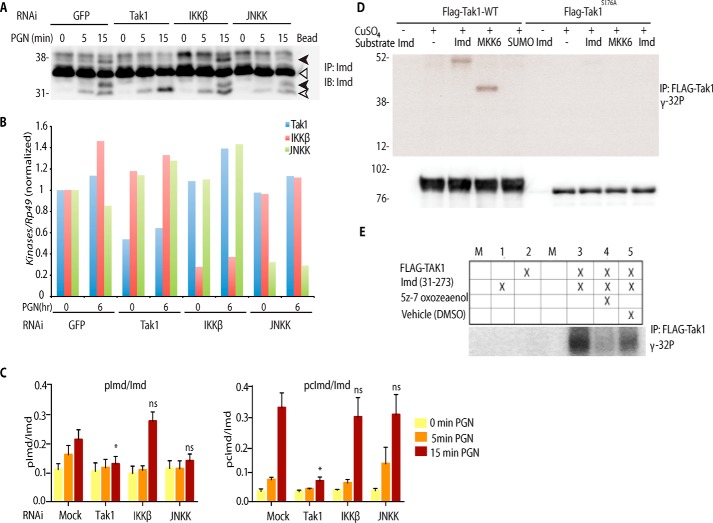
Tak1 directly phosphorylates Imd. A and B, Imd phosphorylation is dependent on Tak1 rather than IKKβ or JNKK. S2* cell were transfected with dsRNA targeting GFP, Tak1, IKKβ (Ird5), or JNKK (Hep) followed by PGN stimulation, as indicated. Endogenous Imd phosphorylation was assayed as above. IP, immunoprecipitated; IB, immunoblotting. B, RNAi efficiency, from the assay displayed in above, was monitored by qRT-PCR. The open triangle marks unmodified full-length Imd, the open arrow marks cleaved Imd, and the black arrow marks phosphorylated Imd. C, immunoblot band intensity ratio from five independent replicate Imd phosphorylation assays, similar to the blot shown above, were quantified. Data are shown as the mean ± S.E., and statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post-test, comparing mock RNAi to each kinase knockdown. *, p < 0.05. ns, not significant. D, Tak1 phosphorylates Imd in vitro. Stable cell lines expressing FLAG-Tak1 WT or S176A (kinase dead) from the Cu2+ inducible metallothionein promoter were treated with CuSO4 (500 μm) for 6 h. FLAG-Tak1 was immunoprecipitated and incubated with [γ-32P]ATP and substrates as indicated. IP samples were also immunoblotted against FLAG-Tak1 as the internal loading control. E, in vitro phosphorylation of Imd is inhibited by the addition o the Tak1 inhibitor, (5Z)-7-oxozeanol, to the reaction. Kinase assays are representative of three independent experiments; M, mock.