Figure 8.
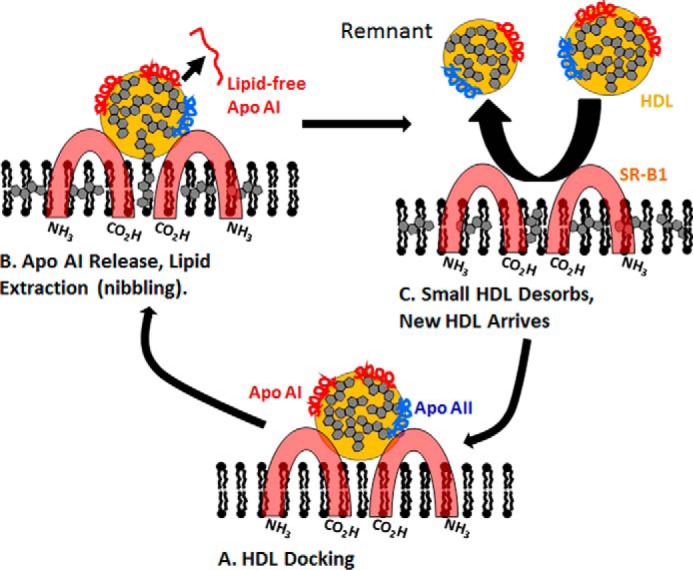
Mechanistic model of SR-B1 nibbling. HDL docks to dimeric SR-B1 (A). During or after docking, a molecule of apoAI is released into the aqueous phase, and one or a few CE molecules enter the non-aqueous channel between SR-B1 dimers after which the CE diffuses through the channel and into the hydrophobic region of the membrane-phospholipid bilayer (B). During this step, the CE content of the bilayer increases, whereas the size of HDL is incrementally reduced (size reduction is exaggerated to emphasize this process), and the smaller, CE-depleted HDL remnant desorbs from the cell and HDL or an HDL remnant, respectively, docks or re-docks to initiate another cycle of CE transfer (C). This model is based on the model of Connelly and Williams (39).
