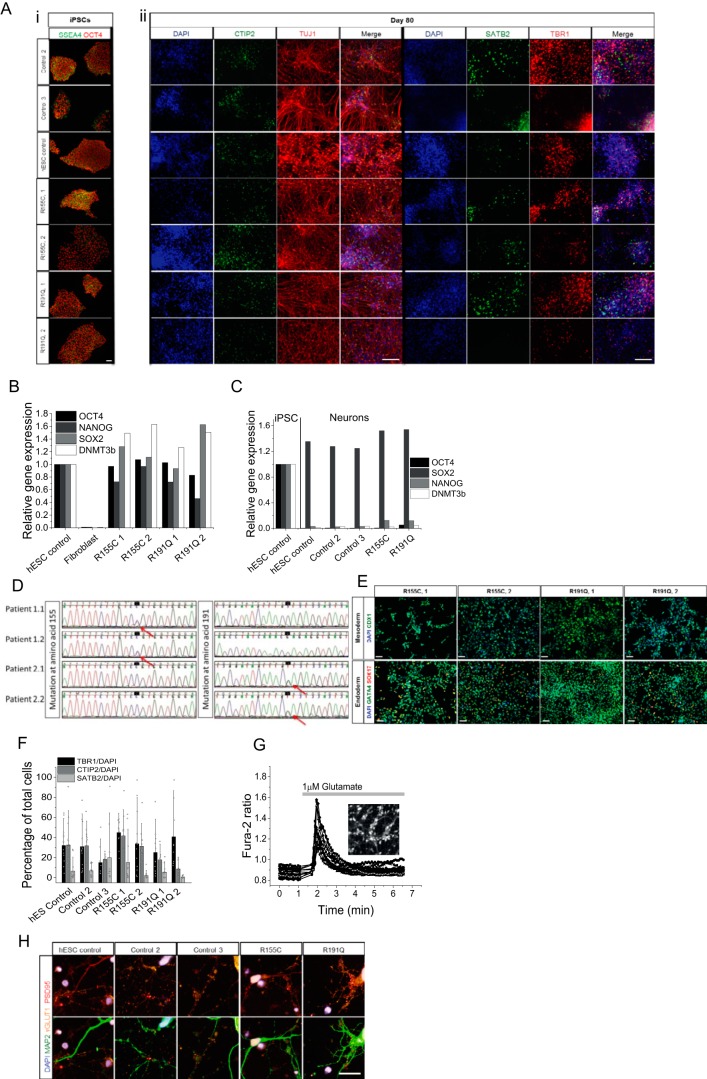
Figure 2.
A, immunocytochemistry showing three control iPSCs and two patient-derived VCP mutant iPSCs lines (2 clones each). All stem cells show expression of pluripotency markers OCT4 and SSEA4 in stem cell conditions and have characteristic colony morphology. By day 80 of differentiation, β-III-tubulin positive neurons are formed expressing markers of deep (TBR1), middle (CTIP2), and upper (SATB2) cortical neurons. Size bar = 100 μm. B, qPCR analysis of four pluripotent stem cell markers in VCP patient-derived iPSCs and control fibroblasts, normalized to three housekeeping genes. C, qPCR analysis to represent faithful silencing of pluripotency genes in neuronal cultures, relative to hESC controls. D, DNA sequencing of iPSC-derived neuron genomic DNA showing mutated nucleotides corresponding to amino acid residues 155 and 191 (arrows). E, monolayer directed differentiation, showing the ability of newly derived iPSC lines to enter the endoderm and mesoderm differentiation pathways. Size bar = 50 μm. F, automated counting of mature neuronal markers displays no difference in the ability of control and VCP iPSCs to form deep (TBR1), middle (CTIP2), and upper (SATB2) layer cortical neurons. G, representative traces of Fura-2-loaded iPSC-derived neurons showing a transient cytosolic calcium response to physiological concentrations of glutamate. Representative image depicts iPSC-derived neurons loaded with Fura-2. H, iPSC-derived neurons express markers of glutamatergic neurons (vGLUT1) and functional synapses (PSD95). Size bar = 20 μm.