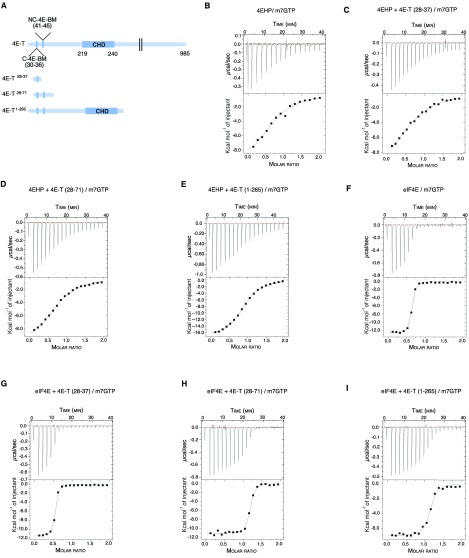
Fig. S4.
Thermodynamic parameters for the interaction of 4EHP and eIF4E with m7GTP in presence of 4E-T peptides. (A) Schematic diagram of full-length 4E-T and 4E-T peptides used in ITC experiments. The canonical (C), noncanonical (NC), and Cup-homology domain (CHD) of the 4E-T protein are depicted. We used three different 4E-T peptides harboring either the canonical YTKEELL motif alone (4E-T28–37), in combination with the noncanonical motif (4E-T28–71), or covering the entire N-terminal extremity including the eIF4E-binding motifs and the CUP-homology domain (4E-T1–265). The 4E-T peptides were incubated with recombinant 4EHP or eIF4E proteins and titrated with m7GTP. (B–I) ITC profiles of 4EHP + m7GTP (B), 4EHP + 4E-T28–37 + m7GTP (C), 4EHP + 4E-T28–71 + m7GTP (D), 4EHP + 4E-T1–265 + m7GTP (E), eIF4E + m7GTP (F), eIF4E + 4E-T28–37 + m7GTP (G), eIF4E+ 4E-T28–71 + m7GTP (H), and eIF4E + 4E-T1–265 + m7GTP (I). The reaction cell contained 200 μL of 30 μM protein and was titrated with 19 injections of 2 μL of 300 μM m7GTP. B–I, Upper show the raw data (μcal⋅s−1), and B–I, Lower represents the integrated data (kcal⋅mol−1 injectant) of heat changes. The binding isotherm was fit with a binding model that uses a single set of independent sites to determine the thermodynamic binding constants and stoichiometry (see Table 1 for details).