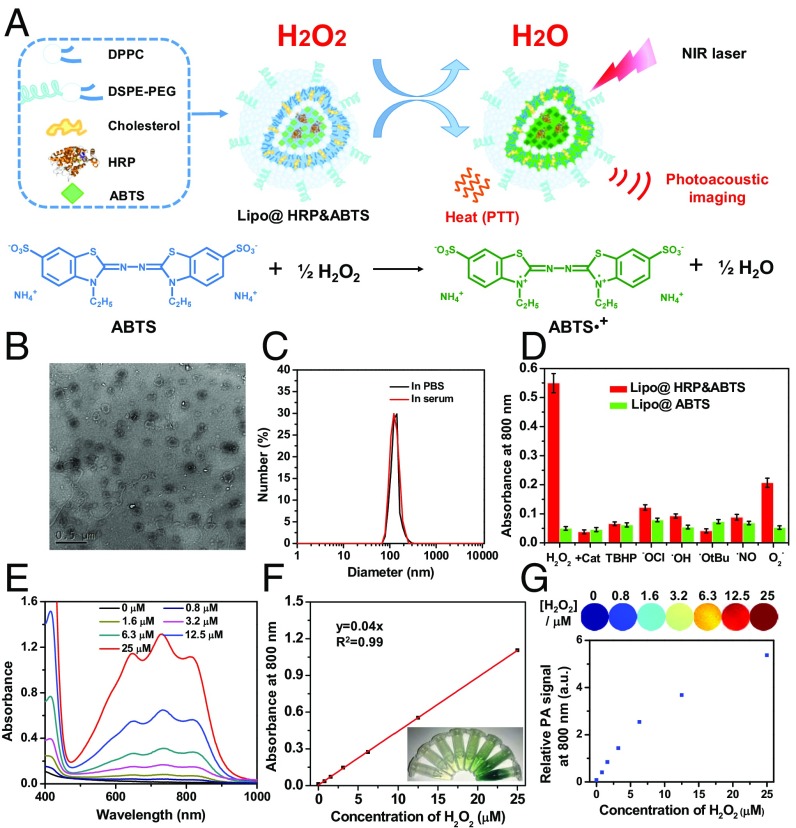
Fig. 1.
Preparation and characterization of Lipo@HRP&ABTS nanoparticles. (A) A schematic illustration showing the formation of Lipo@HRP&ABTS and its applications in H2O2 detection by PA imaging and H2O2-activated photothermal therapy. (B) A TEM image of Lipo@HRP&ABTS. (C) Hydrodynamic diameters of Lipo@HRP&ABTS dispersed in PBS and serum. (D) Absorbance of Lipo@HRP&ABTS or Lipo@HRP&ABTS at 800 nm after incubation with various types of ROS (25 μM) for 30 min. H2O2 (25 μM) pretreated with Cat (0.2 mg/mL) was used as the negative control. (E and F) UV-vis–NIR absorbance spectra (E) and absorbance at 800 nm (F) of Lipo@HRP&ABTS (containing 0.069 mg/mL ABTS and 0.0148 mg/mL HRP) dispersed in buffers with different H2O2 concentrations. (Inset) A photo of those solutions. (G) PA images (Top) and PA signal intensities at 800 nm (Bottom) of Lipo@HRP&ABTS (containing 0.069 mg/mL ABTS and 0.0148 mg/mL HRP) dispersed in buffers with different H2O2 concentrations. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM.