Figure 3.
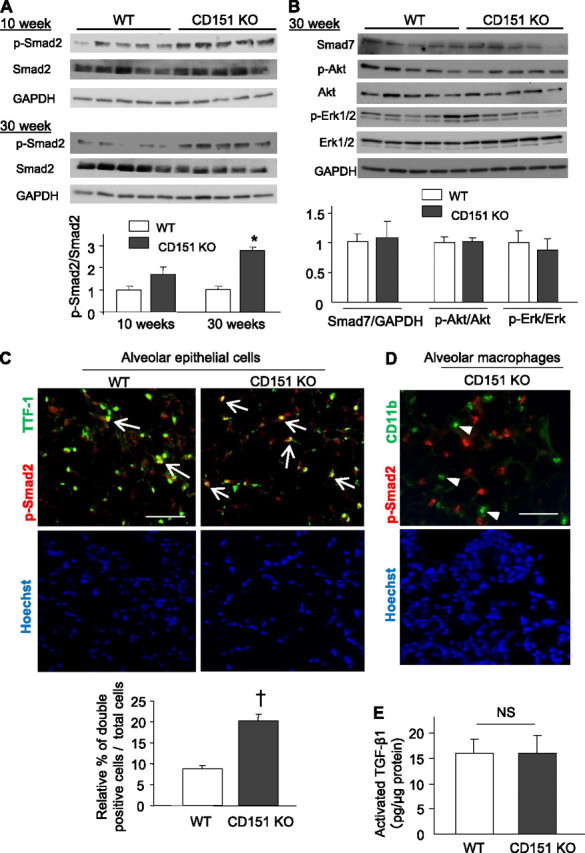
Enhanced p-Smad2 signaling in the alveolar epithelial cells (AECs) of CD151 knockout (KO) mice. (A) Western blot analysis and densitometric quantification of p-Smad2 in total protein homogenates from wild-type (WT) and CD151 KO lungs. Values of p-Smad2 were normalized against total Smad2. *P < 0.001. (B) Western blot analysis and densitometric quantification of Smad7 and p-Akt in total protein homogenates from WT and CD151 KO lungs. Values of Smad7, p-Akt, and p-Erk1/2 were normalized against GAPDH, Akt, and Erk, respectively. (C, D) Immunofluorescence of mouse lungs stained for p-Smad2 and TTF-1 or CD11b. The numbers of p-Smad2 and TTF-1 double-positive AECs (arrows) were significantly larger in CD151 KO lungs (C, n = 4 per group, †P < 0.05). p-Smad2−positive signals were scarcely seen in CD11b-positive alveolar macrophages (D, arrowheads). Bar = 100 μm. (E) Activated TGF-β1 in whole lung was measured by ELISA and normalized against total protein. Levels of activated TGF-β1 were comparable between WT and CD151 KO lungs (n = 3 per group).
