Figure 7.
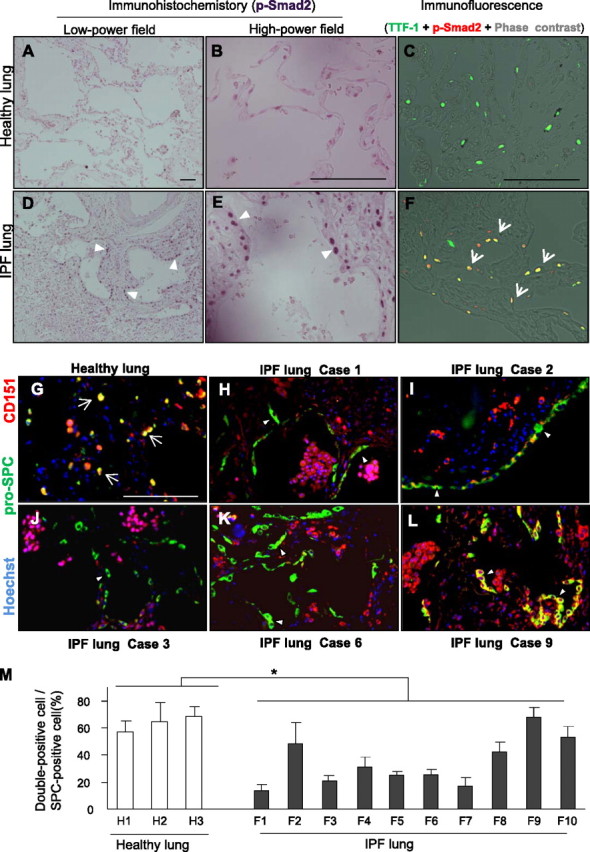
CD151 expression is significantly decreased in alveolar epithelial cells (AECs) from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). (A−F) IPF lungs contained more p-Smad2 signals than healthy lungs (A, D, arrowheads). P-Smad2−positive signals of IPF lungs were preferentially observed in nuclei of AECs (B, C, E, and F, arrowheads and arrows). Representative IPF and healthy lung sections were shown. Bar = 100 μm. TTF-1 = specific marker for type II AECs. (G−L) Representative immunostaining of pro-SPC and CD151 in healthy (n = 3) and IPF (n = 10) lungs. Most AECs expressed CD151 in healthy lungs (G, arrows), whereas CD151-negative AECs were prominent in the lungs of IPF cases 1, 2, 3, and 6 (H−K, arrowheads). Notably, clear and diffuse expression of CD151 was observed in AECs in the lung of case 9 (L, arrowheads). Bar = 100 μm. (M) In histological quantification, at least three fields from each lung were randomly chosen, and an average of 50 pro-SPC–stained AECs per field were quantitated. The number of CD151-positive AECs was significantly decreased in the lungs of patients with IPF (F1−10) compared with healthy lungs (H1−3, *P < 0.05).
