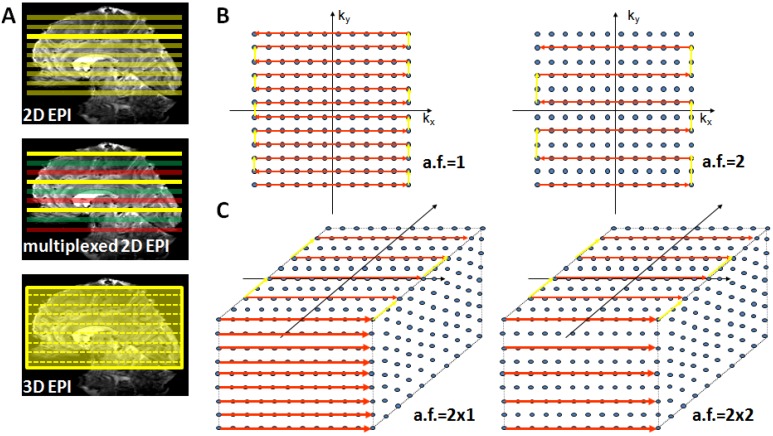
Figure 3.
Suitable echo-planar imaging (EPI) sampling schemes for high-field fMRI. Panel (A) top: Conventional 2D EPI where every slice is excited and acquired separately; middle: in multiplexed EPI several slices are excited simultaneously (colors indicate slice groups), allowing an acquisition speed-up given by the multiplexing factor; bottom: in 3D EPI the slice direction is replaced by a secondary phase encoding direction and the entire volume is continuously excited. With full sampling the speed is identical to 2D EPI, but parallel undersampling along kz is now possible and allows substantial repetition time (TR) reductions. Panel (B) illustrates full (left) and factor-two accelerated (right) in-plane k-space sampling with 2D EPI. Panel (C) shows 3D EPI sampling schemes with factor 2 × 1 (left) and factor 2 along both primary (ky) and secondary (kz) phase encoding direction (right).