Figure 7.
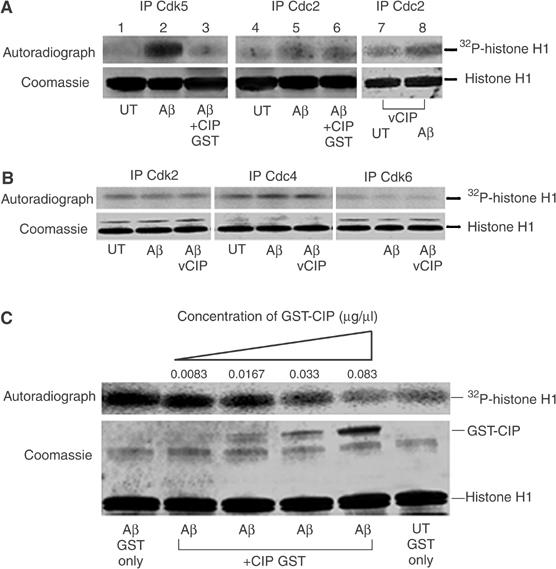
CIP did not affect endogenous neuronal Cdc2 activity nor the activity of other cyclin-dependent kinases, but inhibited Cdk5 hyperactivity in a dose-dependent manner. (A) 7-DIC cortical neurons were treated with 10 μM Aβ1−42 or PBS (UT) for 6 h and subjected to in vitro kinase assays using 5 μg GST-CIP to investigate its inhibitory properties. Cdk5 was immunoprecipitated using C-8 antibody and Cdc2 was immunoprecipitated using the PSTAIRE antibody. In lanes 7 and 8, we infected CIP prior to treatment with Aβ1−42 for 6 h, immunoprecipitated Cdc2 and performed histone H1 kinase assays. The top panel shows the autoradiograph, while the bottom panel shows Coomassie-stained histone H1 bands. (B) 7-DIC cortical neurons were infected with the CIP expression construct using the lentiviral system (lane 3 only) and neurons were treated with 10 μM Aβ1−42 or PBS (UT) for 6 h. Endogenous Cdk2, Cdk4 and Cdk6 were immunoprecipitated from equal amounts of lysates and immunoprecipitates were then subjected to in vitro histone H1 kinase assays. The top panel shows the autoradiograph while the bottom panel shows Coomassie-stained histone H1 bands. (C) CIP affects p25/Cdk5 activity in a dose-dependent manner. Cdk5 was immunoprecipitated using C-8 antibody from equal amounts of lysates of cortical neurons treated or untreated with 10 μM Aβ1−42 for 6 h. Immunoprecipitates were then subjected to in vitro histone H1 kinase assays with the addition of increasing amounts of GST-CIP in a reaction volume of 60 μl. The top panel is the autoradiograph and the bottom panel shows the corresponding Coomassie-stained histone H1 bands. GST-CIP titration experiments were reproducible in four separate assays.
