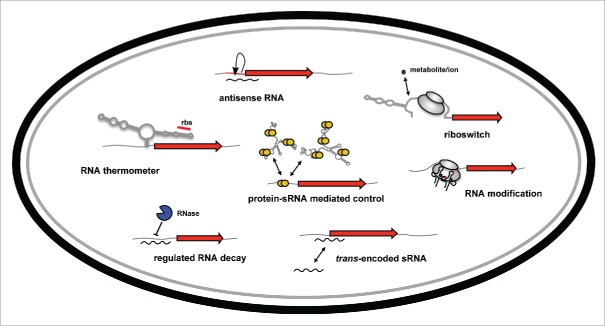
Figure 1.
Overview of RNA-based control mechanisms employed by enteric pathogens of the family Enterobacteriaceae. mRNA translation can be controlled by RNA thermometers and by riboswitches within the 5′-UTR of target mRNAs in response to temperature or metabolites. Transcription, translation and/or stability of target transcripts can be modulated by cis-encoded asRNAs or trans-encoded ncRNAs. The RNA-binding protein CsrA modulates mRNA expression by interfering with translational initiation. The CsrB and CsrC RNAs counteract its activity. RNases control processing and degradation of ncRNAs and target transcripts. RNA-modifying enzymes change the efficiency of translation.