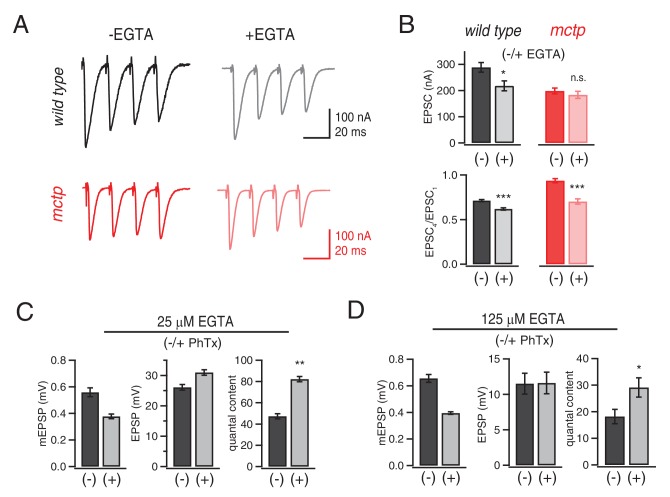
Figure 7. Evidence that MCTP is necessary for the release of an EGTA-sensitive pool of synaptic vesicles.
(A) Representative EPSC traces shown for wild type and mctpOG9 (black and red , respectively) in the absence and presence of EGTA-AM as indicated. (B) Average EPSC amplitudes and short-term modulation of EPSC amplitude (fourth EPSC / first EPSC) for wild type and mctpOG9 in the presence (+) or absence (−) of EGTA as indicated (sample size for wild type: (-EGTA) n = 12, (+EGTA) n = 11; for mctp: (-EGTA) n = 10, (+EGTA) n = 10). (C) Average mEPSP amplitude, EPSP amplitude and quantal content for wild type in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 25 µM EGTA, as indicated. Sample sizes as follows: -PhTx, n = 7; +PhTx, n = 4. (D) Recordings as in (C) performed in the presence of 125 µM EGTA-AM and the presence or absence of PhTx as indicated. Sample sizes as follows: -PhTx, n = 13; +PhTx, n = 15.