Figure 3.
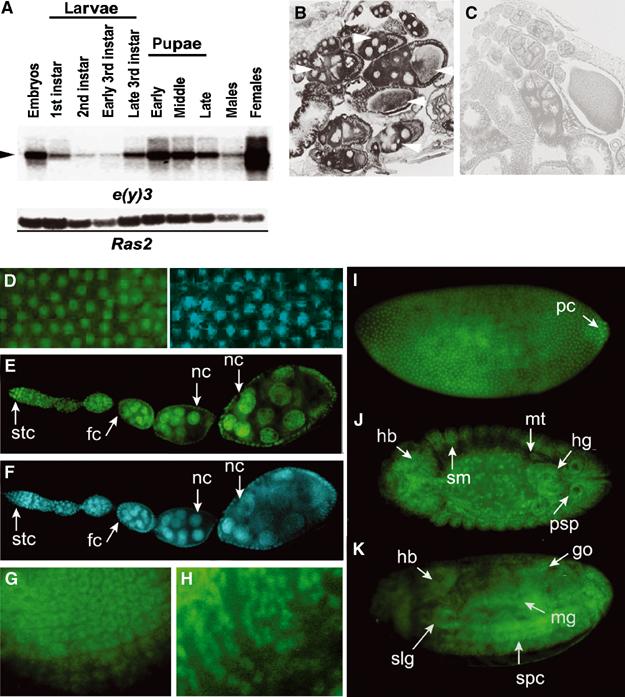
SAYP is a ubiquitous nuclear protein. (A) Northern blot hybridization of poly(A) RNA from different stages of Drosophila development. The 10-kb mRNA is indicated by an arrowhead. The lower panel shows the hybridization of the same membrane with the Ras2 probe. (B, C) In situ hybridization of a frontal tissue section of wt female abdomen with antisense (B) and sense (C) e(y)3 mRNA probes. Arrows indicate wt oocytes and accompanying nursing cells at different stages of development. (D) A field of stage-4 embryo stained with antibodies against SAYP (left) and DAPI (right). The localization of SAYP in the nuclei of syncytium blastoderm is well observed. (E) The distribution of SAYP in adult ovaries. (F) The same stained with DAPI. SAYP is detected in the nuclei of germarium stem cells (stc), follicular cells (fc), and nursing cells (nc). (G, H) SAYP is present in ommatidia precursors of eye-antennal imaginal disk (G) and in precursors of glial cells in the brain of third-instar larva (H). (I–K) SAYP is detected in different tissues of Drosophila embryo. Immunostaining of embryos at stage 4 (I); stage 14, dorsal view (J); and stage 16, ventrolateral view (K). hb, head brain; hg, hindgut; go, gonads; mt, malpigian tubes; mg, midgut; pc, polar cells; psp, posterior spiracles; slg, salivary glands; sm, somatic mesoderm; spc, spinal cord. All embryos are oriented to the left. Affinity-purified Ab1 and FITC-conjugated secondary antibodies were used.
