Figure 1.
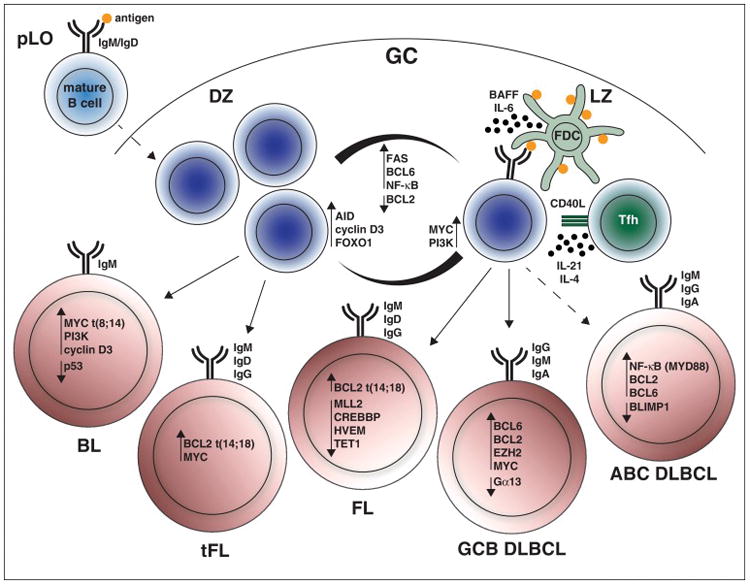
The germinal center reaction and cell of origin in germinal center-derived B lymphomas. In the germinal center (GC), GC B cells undergo clonal expansion in the dark zone (DZ) and are positively selected in the light zone (LZ). In the LZ, follicular dendritic cells (FDC) retain antigen and cooperate with follicular helper T (Tfh) cells to support competitive GC B cells for survival and either differentiation or iterative rounds of cell division in the DZ. Several pathways are differentially regulated in DZ and LZ GC B cells. Mutations in these pathways manifest to different degrees in human B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL) derived from GC B cells. The oncogenic potential of the highlighted pathways has been mechanistically assessed in murine models of B-NHL.
