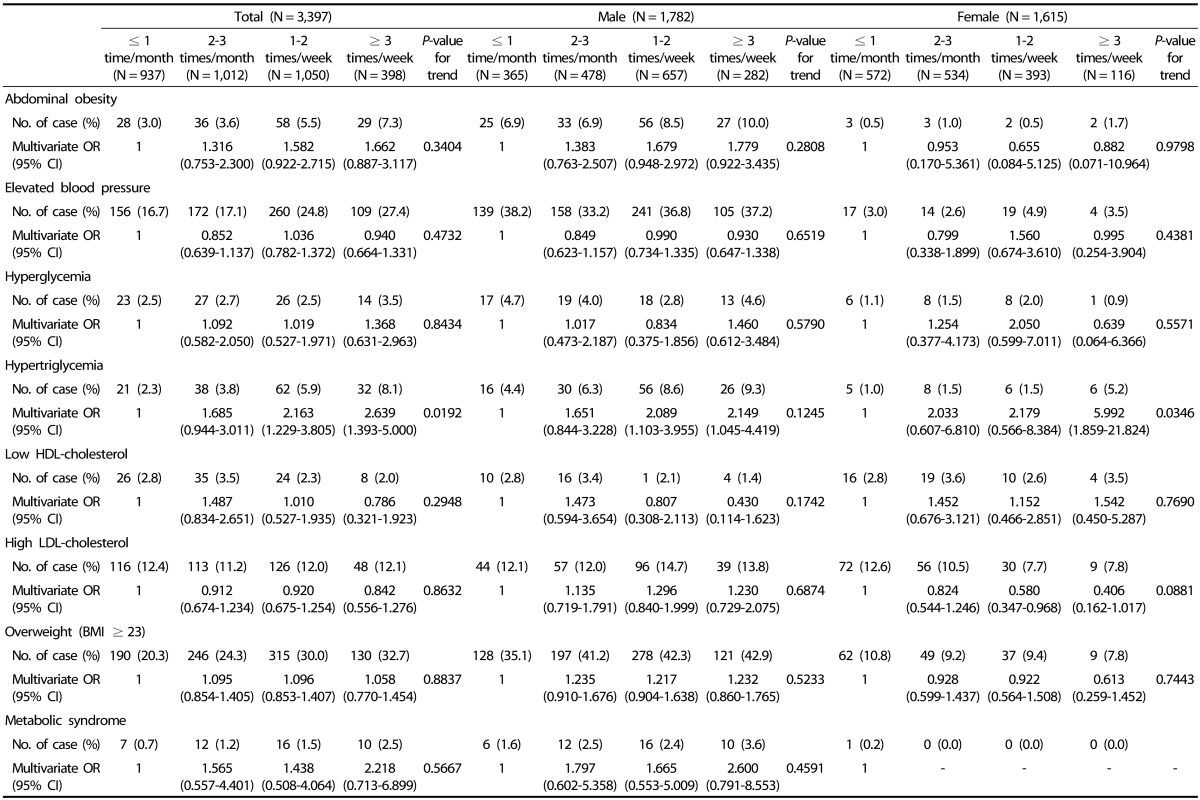
Table 4. Multivariate odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for cardiometabolic risk factors according to the frequency of instant noodle consumption1).
1)Determined by multivariate logistic regression analysis after controlling for age, BMI, gender, family income (< 2000 US $/mo, 2000-4000 US $/mo, > 4000 US $/mo), alcohol consumption (non-drinker, moderate drinker, heavy drinker), smoking behavior (non-smoker, ex-smoker, current smoker), physical activity (low, moderate, high), and consumption frequency of fruits, vegetables, milk and dairy products, high-fat fish, high-fat and processed meats, sweets and confectionery, carbonated beverages (≤ 1 time/month, 2–3 times/month, 1–2 times/week, ≥ 3 times/week).
Reference values according to the Adult Treatment Panel III of the National Cholesterol Education Program (abdominal obesity: males ≥ 90 cm, females ≥ 85 cm; elevated blood pressure: SBP ≥ 130 mmHg or DBP ≥ 85 mmHg, hyperglycemia: FBS ≥ 100 mg/dL; hypertriglycemia: TG ≥ 150 mg/dL, low HDL cholesterol: males < 40 mg/dL, females < 50 mg/dL, high LDL cholesterol: ≥ 130 mg/dL).