Figure 2.
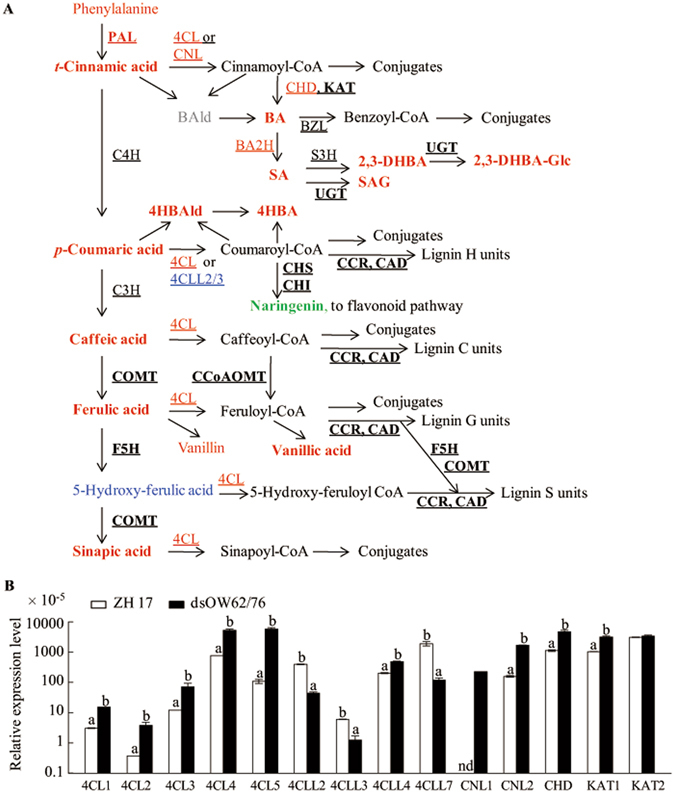
Schematic representation of variations in the phenylpropanoid pathway (A) and gene expressions (B). Free phenolic acids can be activated by ligases (4CLs) to form phenoloyl-CoAs, which may conjugate with amines to produce phenolamides or used as precursors for lignan biosynthesis. Feruloyl-CoA can be converted to coniferaldehyde by caffeic acid 3-O-methyltransferase (CCR) and further to coniferyl alcohol by cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD). Ferulate 5-hydroxylase (F5H) can catalyze the 5-hydroxylation of coniferaldehyde and coniferyl alcohol and then the products are methylated by caffeic acid/5-hydroxyferulic acid O-methyltransferase (COMT) to produce sinapaldehyde and sinapyl alcohol. Phenoloyl-CoAs generated by ligase like enzymes (4CLLs, or CNLs) in peroxisome may go through β-oxidative pathway to form benzenoid compounds. The font colors and shapes represent the same meanings as described in Fig. 1. The chemicals in bold were the compounds labeled by isotopes in the [2H8]Phe feeding experiments. A rice ubiquitin gene was used as the internal standard for qPCR analysis. Experiments were performed twice with similar results. Values marked with different letters indicate statistically significant differences as analyzed by SAS software (Duncan’s multiple range test, α = 0.05). nd for undetectable. Abbreviations: BA, benzoic acid; BAld, benzaldehyde; 2,3-DHBA, 2,3-dihydroxy BA; 2,3-DHBA-Glc, 2,3-DHBA glucoside; 4HBA, 4-hydroxy benzoic acid; 4HBAld, 4-hydroxy benzaldehyde; SA, salicylic acid; SAG, SA glucoside; BA2H, BA 2-hydroxylase; BZL, benzoyl-CoA:ligase; C3H, p-coumarate 3-hydroxylase; C4H, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase; CCoAOMT, caffeoyl-CoA 3-O-methyltransferase; 4CL, 4-coumaroyl-CoA:ligase; 4CLL, 4CL like; CNL, cinnamoyl-CoA:ligase; CHD, cinnamoyl-CoA hydratase-dehydrogenase; CHI, chalcone isomerase; CHS, chalcone synthase; KAT, 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase; PAL, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase; S3H, SA 3-hydroxylase; UGT, UDP-glycosyltransferase.
