Figure 4.
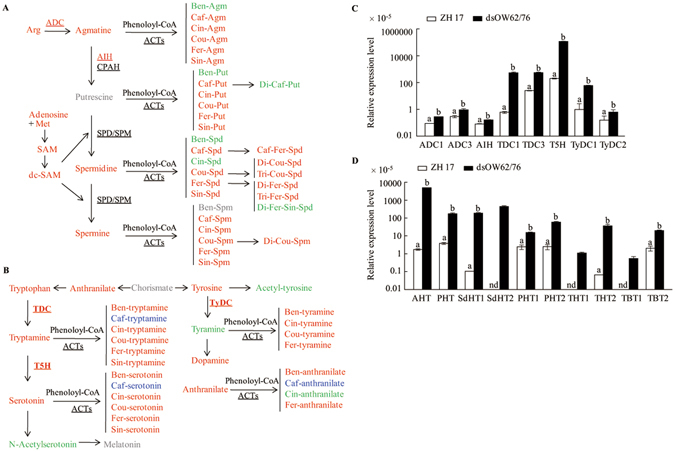
Enhanced accumulation of phenolamides derived from aliphatic (A) and aryl (B) amines and upregulation of the related genes (C,D) in dsOW62/76 plants. (A) Polyamines (PAs) and agmatine can be conjugated with phenoloyl-CoA to form phenolamides. Similarly, the arylamines derived from chorismate can be converted to phenolamides (B). The font colors and shapes represent the same meanings as described in Fig. 1. Transcription levels of the genes for amine generation (C) and for phenolamide formation (D) were analyzed. Data are means ± SE of three replicates. A rice ubiquitin gene was used as the internal standard for qPCR analysis. Values marked with different letters indicate statistically significant differences as analyzed by SAS software (Duncan’s multiple range test, α = 0.05). nd for not detected. Abbreviations: Agm, Put, Spd, and Spm for agmatine, putrescine, spermidine, and spermine, respectively; Ben, Caf, Cin, Cou, Fer, and Sin for benzoyl, caffeoyl, cinnamoyl, coumaroyl, feruloyl, and sinapoyl, respectively; dc-SAM decarboxylated S-adenosylmethionine; SAM S-adenosylmethionine; ACTs, N-acyltransferases, in which AHT, PHT, SdHT, and THT for Agm, Put, Spd, and tryptamine hydroxycinnamoyl transferases, respectively and TBT for tryptamine benzoyl transferase; ADC, arginine decarboxylase; AIH, agmatine iminohydolase; CPAH, N-carbamoylputrescine amidohydrolase; SPD/SPM, spermidine/spermine synthase; T5H, trytamine 5-hydroxylase; TDC, tryptophan decarboxylase; TyDC, tyrosine decarboxylase.
