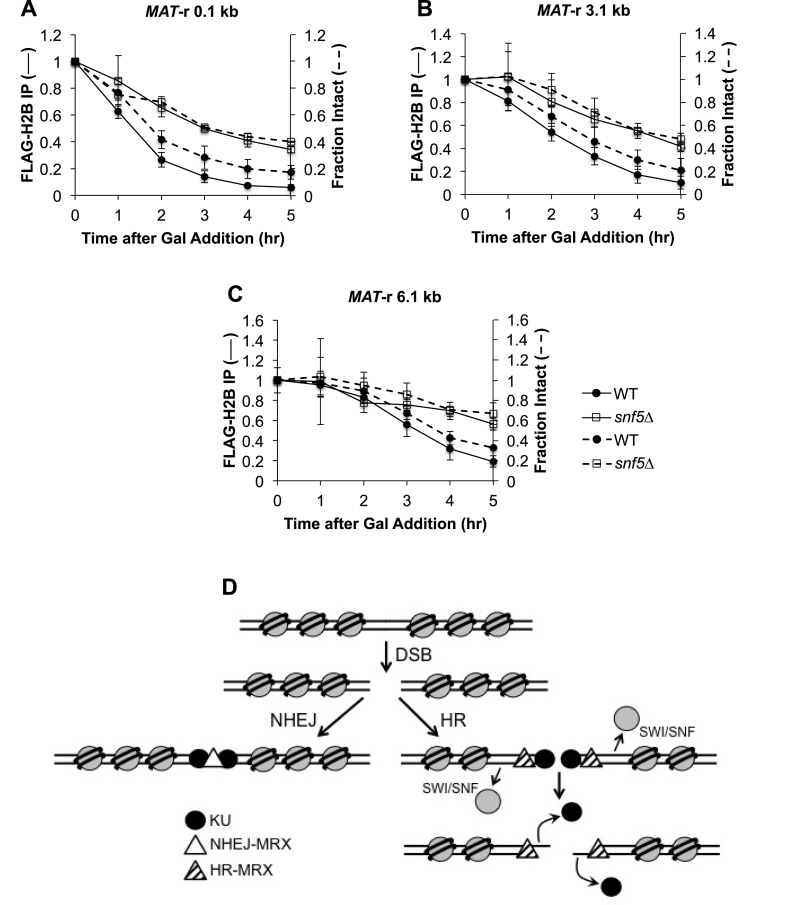
Figure 5.
Nucleosome eviction at MAT is delayed in snf5Δ cells. Asynchronous WT (n = 4) and snf5Δ (n = 3) cells containing FLAG-H2B were harvested at 1 h intervals after addition of galactose to induce a MAT DSB. H2B eviction was monitored by ChIP (solid lines) using qPCR with primers that anneal (A) 0.1 kb; (B) 3.1 kb and (C) 6.1 kb to the right of the DSB, and resection was simultaneously monitored (dashed lines). Error bars denote one standard deviation. (D) Model for role of SWI/SNF in the initiation of HR repair. Only initial events in the repair of a DSB by NHEJ or HR are shown. After a DSB is formed, KU rapidly associates with broken ends and recruits Dnl4-Lif1, leading to the recruitment of a pool of NHEJ-MRX that tethers broken ends and stimulates end ligation that is essential for repair by NHEJ (left panel). Recruitment of SWI/SNF to a DSB promotes nucleosome eviction in the vicinity of the break, leading to the recruitment or stabilization of a distinct pool of HR-active MRX (right panel). The nuclease activity of MRX promotes the initiation of end resection, which leads to the displacement of KU. Long-range resection factors, Exo1 and Dna2–STR, are then recruited, the ssDNA overhang is coated with RPA, and the DNA damage checkpoint is activated. RPA is replaced with the Rad51 recombinase and the nucleoprotein filament initiates homology search for HR repair.