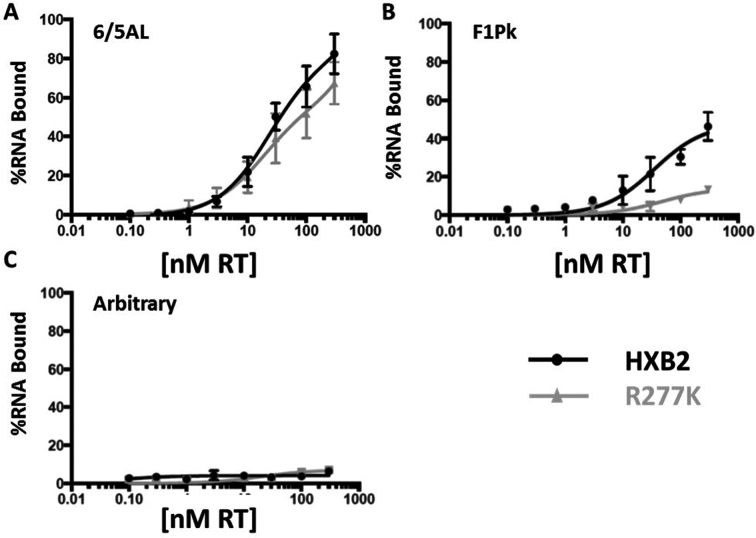
Figure 3.
Aptamer–RT binding. The 6/5AL aptamer (A), F1Pk (B) and arbitrary aptamer (C) were 5΄-end labeled with 32P-ATP and added to aptamer–RT binding reactions containing various concentrations of subtype B RT or the R277K point mutant in binding buffer. Aptamer–RT binding reactions were incubated on ice for 15 minutes and reactions were then loaded onto pre-wet nitrocellulose membranes. Samples were allowed to flow through the nitrocellulose membranes via vacuum and aptamer–RT complexes were retained on the membrane. Radioactivity was determined via scintillation counter. The 0 nM RT reaction was used as a control and the amount of radioactivity present in the unfiltered sample was set to 100%. The protein-dependent signal was determined by subtracting the value obtained for the 0 nM control from the value obtained for the sample. Values at each RT concentration were fit into a one-site binding graph using Prism software version 6.2. For the 6/5AL aptamer, Kd values under the conditions of these assays were 81 nM for subtype B RT and 57 nM for the R277K point mutant.