Figure 5.
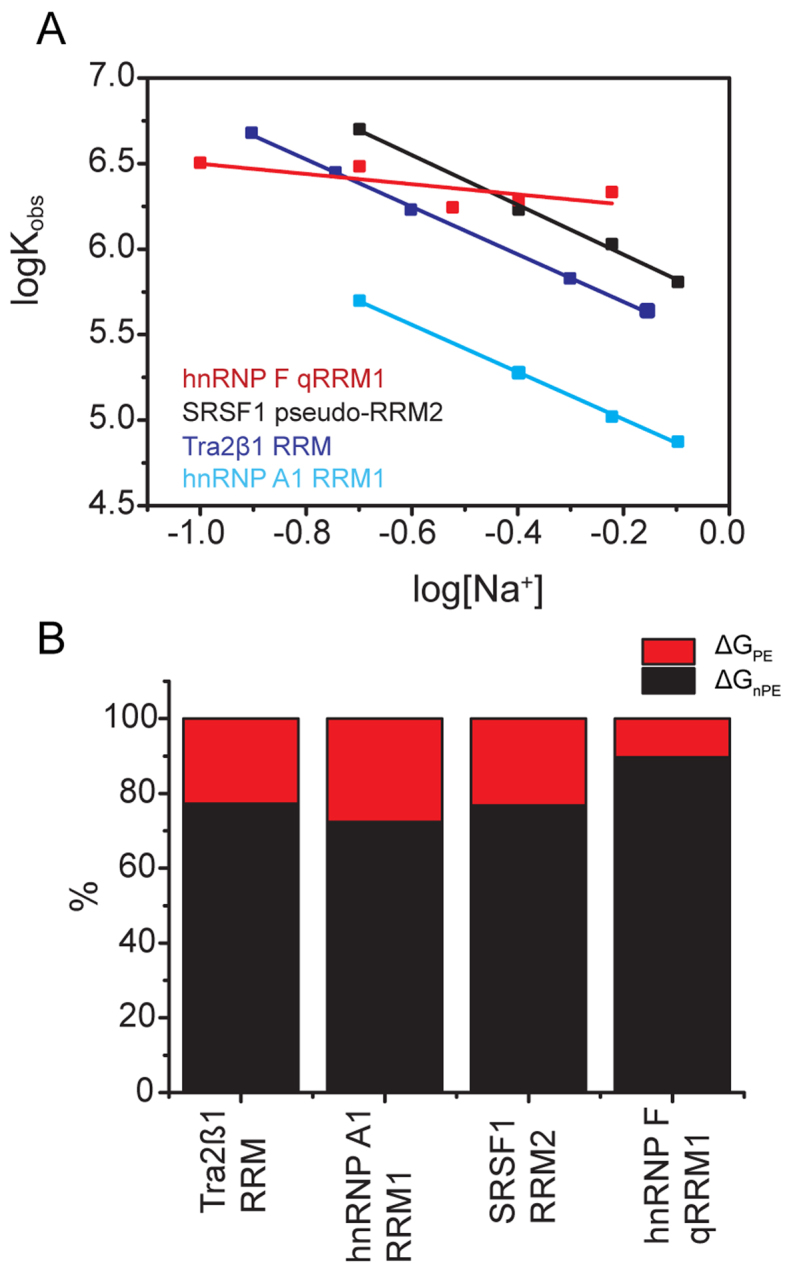
Non-polyelectrolyte (‘non-electrostatic’) effects are the general force driving cognate RNA recognition by different RNA binding modes. (A) Variation of the logarithm of the association constant Kobs as function of concentration of Na+ ions (log[Na+]) upon formation of RRM–ssRNA complexes. The data were collected by ITC by injecting 100–500 μM free RRMs into 5–25 μM cognate RNAs at 10°C temperature, in 20 mM CH3COOH, 50 mM L-arginine, 50 mM L-glutamate, 0.05% β-mercaptoethanol–NaOH pH 5.5, at various concentrations of NaCl. (B) Partitioning of the overall free energy. The graph shows the percentage electrostatic contribution due to ion-release (ΔGPE), as well as the contribution from non-polyelectrolyte effects (ΔGnPE). The components were calculated from data shown in (A).
