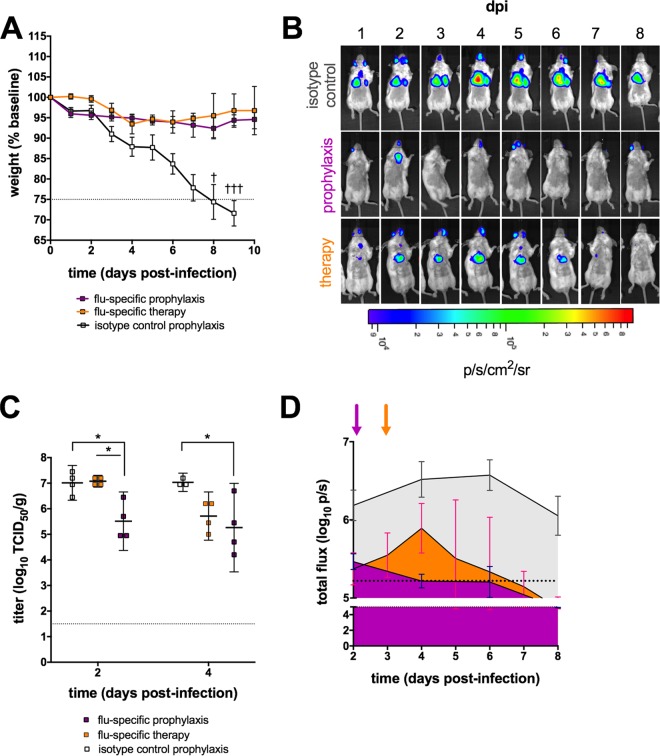
FIG 4 .
Bioluminescence in vivo imaging of passively immunized mice. An influenza virus-specific hMAb (EM4CO4) was administered either prophylactically (24 h prechallenge) or therapeutically (72 h postchallenge). Mice that received prophylaxis with an equivalent dose of isotype control antibody (human IgG1κ) are shown for comparison. (A to C) Weight loss (A); a bioluminescence imaging series of a single representative mouse from each group, expressed in photons per second per square centimeter per steradian (p/s/cm2/sr) (B); and virus titers in the lungs (C) are shown. (D) The mean bioluminescence in each group (four mice per group) is plotted for each time point indicated, and the area under the curve for each group is shaded to highlight differences in flux kinetics (photons per second). Magenta, prophylaxis; orange, therapy; gray, isotype control prophylaxis. Shaded arrows indicate the timing of antibody administration for each group that received influenza virus-specific antibody. Dashed lines indicate the threshold for euthanasia due to weight loss associated with infection (A), the limit of detection of infectious virus (C), or the limit of detection of the bioluminescent signal (D). *, P < 0.05.