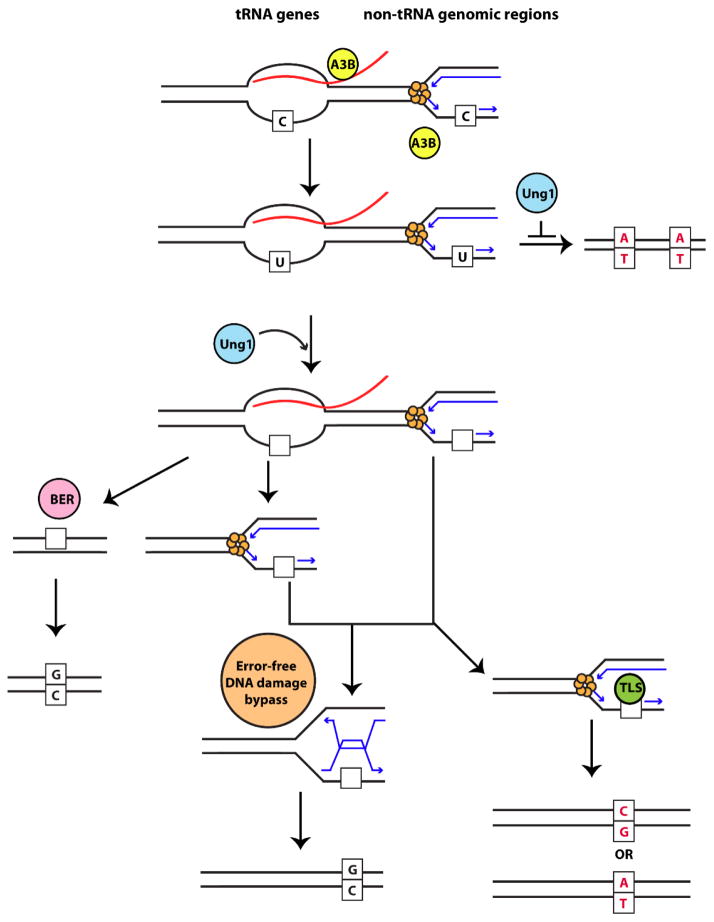
Fig. 4. Model for A3B-induced mutagenesis and repair in tRNA genes and non-tRNA genomic regions.
ssDNA mutated by A3B (yellow circle) in tRNA genes is stabilized by RNA:DNA hybrids formed during transcription (red = RNA) while in other genomic regions ssDNA is formed on the lagging strand during DNA replication (blue arrows). Moreover, the RNA transcript at tRNA genes could directly recruit A3B to the ssDNA formed during transcription. In the absence of Ung1 (blue circle), replication across dU residues leads to a C→T transition (red). Ung1 (blue circle) can act on dU residues and form abasic sites in DNA (empty squares). In tRNA genes, removal of RNA leads to reannealing of the strands, and base excision repair machinery (pink circle) can repair the abasic site in an error-free manner. On the other hand, persistent RNA:DNA hybrids, would prevent repair by BER, and abasic site would later be presented as a block to the replication fork. Abasic sites at the fork, can either be undergo error-free repair by the error-free DNA damage bypass pathway (orange circle) or are bypassed by translesion synthesis polymerases (green circle) which can lead to C→T or C→G substitutions (red).