Fig. 1.
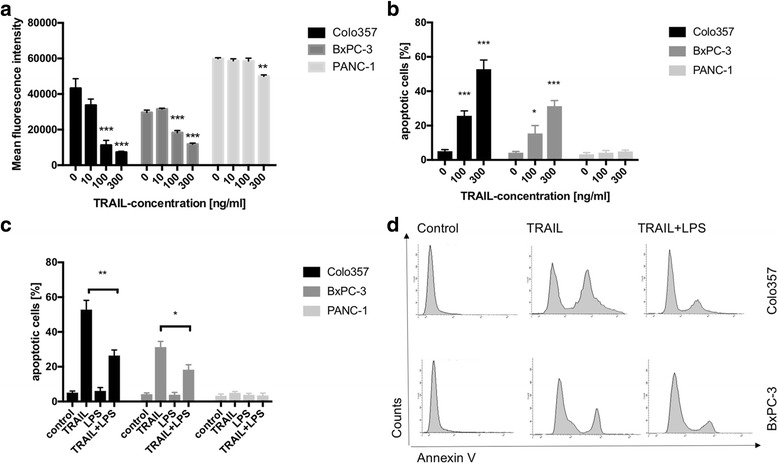
LPS-stimulation promoted resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. a Cells cultures of COLO357, BxPC-3 and PANC-1 were stimulated with TRAIL for 24 h and cell viability was determined using a Cell titer blue assay. Mean fluorescence intensities following TRAIL-stimulation are shown. TRAIL – stimulation decreased viability of COLO 357 and BxPC-3 whereas viability of PANC-1 cells remained almost unchanged. N = 5/group. b Cell cultures of COLO357, BxPC-3 and PANC-1 were TRAIL-stimulated for 24 h and the fraction of apoptotic cells was determined via FACS analyses employing a Annexin V assay. TRAIL-stimulation induced apoptosis in COLO 357 and, to a lesser degree, in BxPC-3 cells, whereas PANC-1 cells were TRAIL-resistant. N = 5/group. c Cell cultures of COLO357, BxPC-3 and PANC-1 were stimulated with 300 ng/ml TRAIL, 1 μg/ml LPS and 300 ng/ml TRAIL + 1 μg/ml LPS for 24 h. Non-stimulated cell cultures served for controls. Thereafter, fractions of apoptotic cells were determined. Co-stimulation with TRAIL and LPS significantly decreased the number of TRAIL-induced apoptotic cells in COLO357 and BxPC-3. N = 5/group. d Representative histograms of FACS analyses employing the Annexin V assay of COLO357 and BxPC-3 are shown. Means and standard errors of the mean are shown. *) p < 0.05; **) p < 0.01; ***) p < 0.001
