Fig. 2.
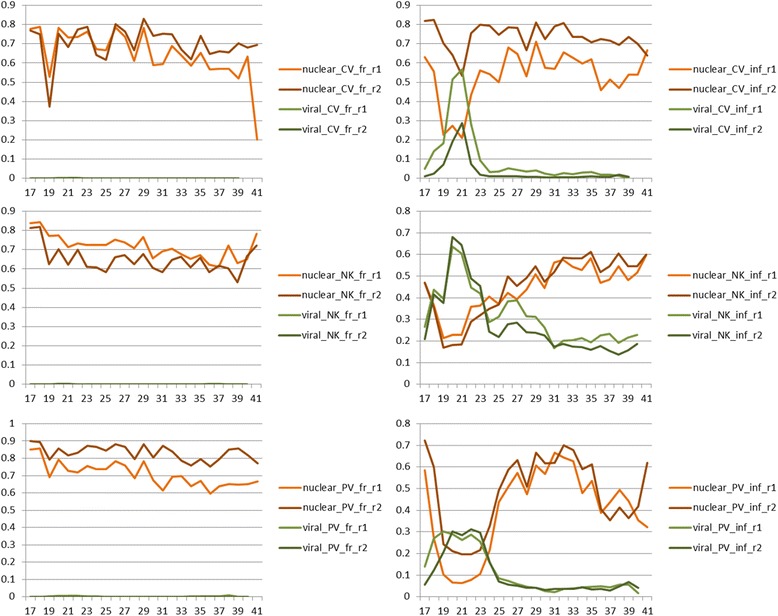
Proportions of reads matching to the reference genomes. The proportions of redundant reads matching to the nuclear genome (y-axis) are shown in orange lines; the proportions relative to the viral genomes are indicated in green lines. On the x-axis we represent the size classes. The proportions of fungal genome matching in virus-free samples were consistently high and the number of incident reads matching to the viral genomes was low (few spurious incident reads were observed). In virus-infected samples the proportion of reads matching to the viral genome peaks in the range of 19–24 nucleotide (nt) reads and corresponds to a drop in the proportions of reads matching to the fungal genome. The overall proportion of reads matched to one of the reference genomes – fungal or viral – is constantly high across all size classes. The CV, NK and PV correspond to Aspergillus fumigatus chrysovirus (AfuCV), a strain of Aspergillus fumigatus tetramycovirus-1 (AfuTmV-1) and Aspergillus fumigatus partitivirus-1 (AfuPV-1), respectively. (CV_fr_r1: AfuCV free isolate replicate-1; CV_fr_r2: AfuCV free isolate replicate-2; CV_inf_r1: AfuCV infected isolate replicate-1; CV_inf_r2: AfuCV infected isolate replicate-2; NK_fr_r1: AfuTmV-1 free isolate replicate-1; NK_fr_r2: AfuTmV-1 free isolate replicate-2; NK_inf_r1: AfuTmV-1 infected isolate replicate-1; NK_inf_r2: AfuTmV-1 infected isolate replicate-2; PV_fr_r1: AfuPV-1 free isolate replicate-1; PV_fr_r2: AfuPV-1 free isolate replicate-2; PV_inf_r1: AfuPV-1 infected isolate replicate-1; PV_inf_r2: AfuPV-1 infected isolate replicate-2)
