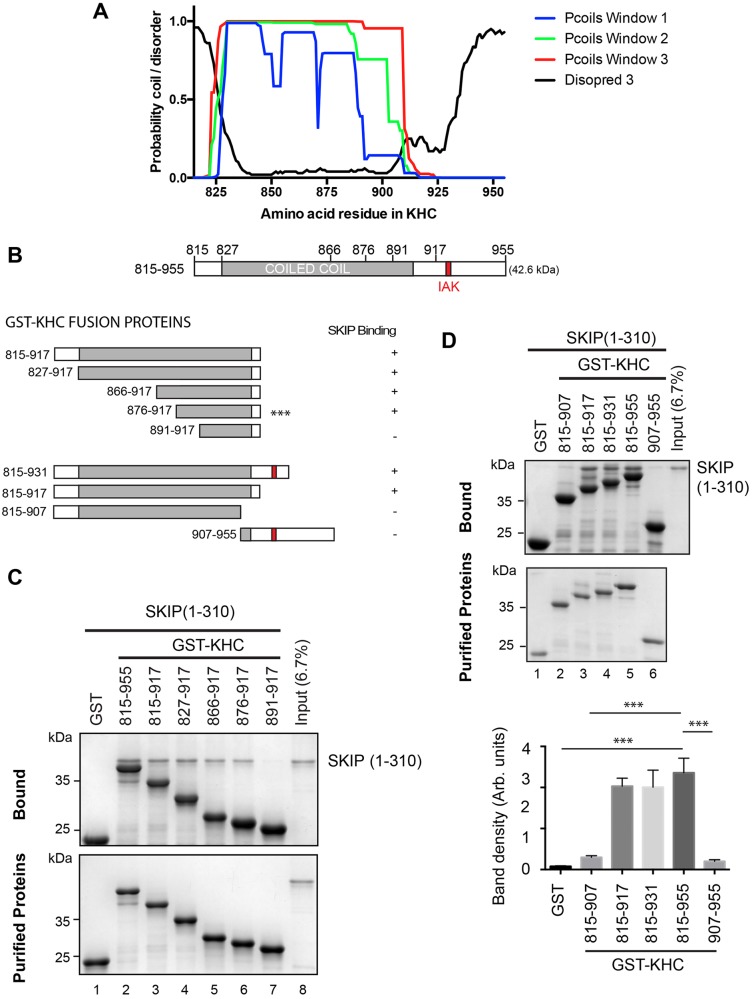
Fig. 2.
SKIP–KHC interaction requires amino acids 876–917 of KHC. (A) Graph and schematic showing structure predictions from Pcoils and Disopred3 for the C-terminal region of KHC. The location of the autoinhibitory IAK motif is highlighted. (B) Schematic of constructs used in this figure with summary of SKIP(1-310)-binding capacity. *** indicates the minimally defined SKIP-binding segment of KHC. (C) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gels from a GST pulldown experiment using a series of truncations of KHC showing that amino acids 876-917 are sufficient for SKIP(1-310) binding. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (D) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gels from a GST pulldown experiment using a series of truncations of KHC showing that amino acids 908–917 are required for SKIP(1-310) binding. Graph shows mean±s.e.m. of relative binding from three independent experiments. ***P<0.001 (one-way ANOVA and Dunnett's multiple comparison test for comparison to 815–955).