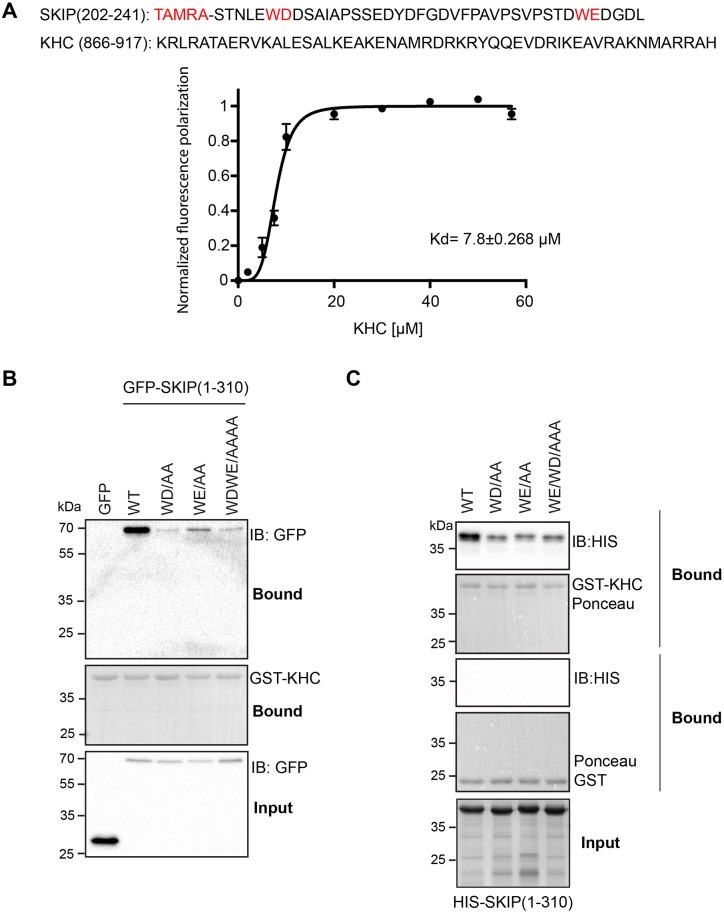
Fig. 4.
Interaction between KHC and SKIP requires both W-acidic motifs. (A) Fluorescence polarization binding assay using a TAMRA-conjugated peptide from SKIP containing both W-acidic motifs. KHC(866-917) was prepared by cleavage of purified GST–KHC(866-917) and removal of free GST or uncleaved protein by incubation with glutathione beads. KHC(866-917) is added at increasing concentration. Error bars show s.e.m. from three replicates and curve shows fit of data to a one-site specific binding model with hill slope [EQ Y=Bmax×Xh/(Kdh+Xh) where Bmax=180.7, Kd=7.878] (h)=4.703. R2=0.98. (B) Western blot (IB) showing GST pulldown experiment from extracts of 293T cells expressing wild-type (WT) GFP–SKIP(1-310) or WD/AA, WE/AA or WDWE/AAAA mutants. Binding is reduced by disruption of either motif. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (C) Western blot showing GST pulldown experiment using purified His6–SKIP(1-310) produced in E. coli. Binding is reduced by disruption of either W-acidic motif. Data are representative of three independent experiments.