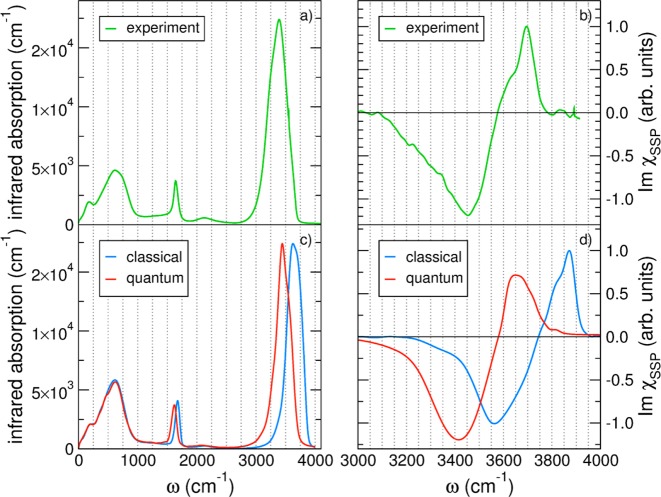
Figure 11.
Comparisons between experimental (top) and simulated (bottom) infrared spectra of liquid water (left) and heterodyne detected vibrational sum-frequency spectra of the air/water interface (right). All simulations were performed using many-body molecular dynamics (MB-MD) carried out at both classical (blue traces) and quantum (red traces) levels using the MB-pol PEF combined with many-body representations of the water dipole moment (MB) and polarizability. On the left panels, χSSP is the resonant sum-frequency susceptibility, and S, S, and P are the components related to the polarization conditions of the sum-frequency, visible, and IR beams, respectively. S and P denote beam polarizations parallel and perpendicular to the surface, respectively. See refs (261) and (90) for specific details.