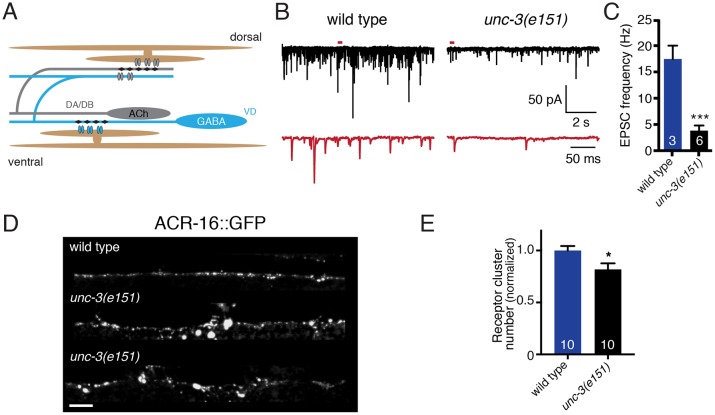
Fig. 1.
Cholinergic neuromuscular transmission is impaired in unc-3(e151) mutants. (A) The C. elegans motor circuit. Excitatory cholinergic motor neurons (gray) synapse onto inhibitory GABAergic motor neurons (blue) and onto body wall muscles (brown). (B) Representative recordings of endogenous EPSCs from body wall muscles of wild-type and unc-3(e151) mutant animals. Red traces are expanded views of time segments under the red bars in the upper traces. (C) The average frequency of endogenous EPSCs recorded from wild type and unc-3(e151) mutants. Each bar represents the mean±s.e.m., and numbers in bars indicate the n for each genotype in this figure and for all subsequent figures. ***P<0.0001; Student's t-test. (D) Confocal images of one wild-type (top) and two unc-3(e151) (middle and bottom) animals expressing GFP-tagged AChRs in body wall muscles (myo3p::ACR-16::GFP). Scale bar: 5 µm. (E) Normalized receptor cluster number per 75 µm of ventral nerve cord. *P<0.05; Student's t-test.