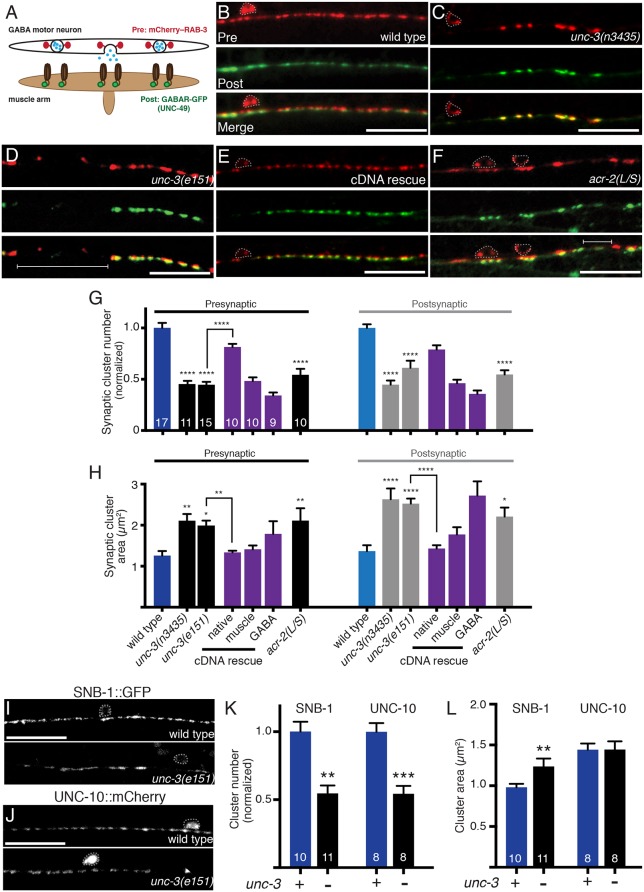
Fig. 4.
Impaired cholinergic innervation alters the distribution and size of GABA synapses. (A) Diagram depicting the location of fluorescent reporters used to label GABA pre- (unc-47p::mCherry::RAB-3) and postsynaptic (UNC-49::GFP) structures. (B-F) Confocal images of the ventral nerve cord in adult wild type (B), unc-3(n3435) mutants (C), unc-3(e151) mutants (D), unc-3(e151) mutants expressing an unc-3 cDNA rescuing array (unc-3p::unc-3 cDNA) (E), and transgenic acr-2(L/S) animals (F) co-expressing unc-47p::mCherry::RAB-3 in GABA motor neurons with UNC-49::GFP in body wall muscles. Note areas devoid of synaptic clusters (brackets) and enlarged clusters in unc-3 mutants and acr-2(L/S) transgenic animals. Motor neuron cell bodies are outlined in this figure and all subsequent figures. Scale bars: 20 µm. (G) Average number of pre- and postsynaptic clusters per 50 µm, normalized to wild type. (H) Average size of pre- and postsynaptic clusters at GABA synapses. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001 compared with either control or unc-3 mutant as indicated; ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparisons test. (I,J) Confocal images of the ventral cord in wild type or unc-3(e151) mutants expressing the GFP-tagged synaptic vesicle marker synaptobrevin (SNB-1::GFP) (I), or the Rim1 homolog (UNC-10::mCherry) (J). Scale bars: 20 µm. (K) Quantification of synaptic cluster number per 50 μm for each marker, normalized to wild type. (L) Quantification of presynaptic cluster area for genotypes indicated. **P<0.01, ***P<0.0001; Student's t-test.