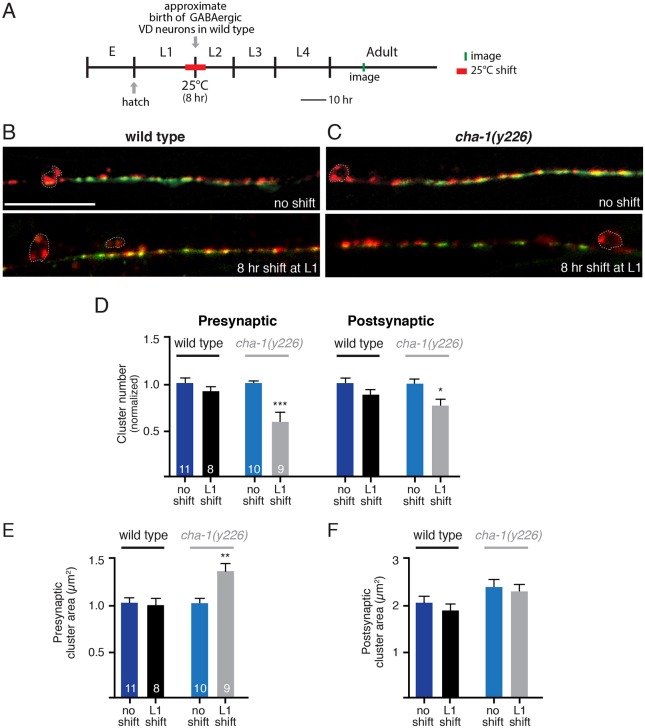
Fig. 8.
Reduced cholinergic neurotransmission during a period of GABAergic synaptogenesis alters GABAergic synaptic connectivity. (A) Diagram indicating predicted timeline of wild-type C. elegans development at 15°C and temperature shifts employed. Approximate time of hatch is indicated. (B,C) Confocal images of the ventral nerve cord in adult wild-type (B) and cha-1(y226) (C) temperature-sensitive mutant animals co-expressing GABA pre- and postsynaptic markers (unc-47p::mCherry::RAB-3 and UNC-49::GFP) grown at the permissive temperature and after an 8 h shift to the non-permissive temperature during the first larval stage. Note that the representative image for the cha-1 no shift control group shown in C is the same as that displayed in Fig. 7C. Scale bar: 20 µm. (D) Average number of GABA presynaptic and postsynaptic clusters per 50 µm for wild type (black) and cha-1(y226) mutants (gray). (E,F) Average size of GABA presynaptic (E) and postsynaptic (F) clusters for wild type (black) and cha-1(y226) mutants (gray). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.0001; Student's t-test.