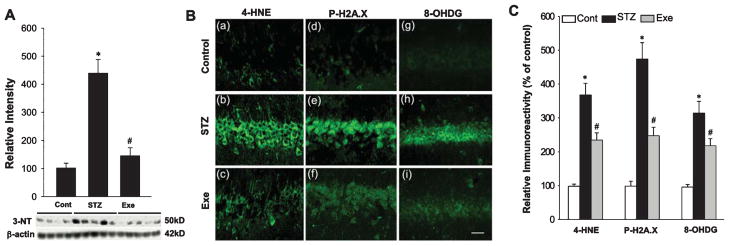
Fig. 5.
Treadmill exercise ameliorates STZ-induced oxidative stress damage. A) Western blot analysis of reactive nitrogen species (RNS) generation, marked by 3-NT. STZ-induced RNS accumulation was markedly attenuated by treadmill exercise during AD progression. B) Confocal analysis for oxidative stress-induced damage to basic cellular components: lipid, histone and DNA, marked by 4-HNE (a–c), P-H2A.X (d–f), and 8-OHDG (g–i) respectively. Note that treadmill exercise significantly attenuated STZ-induced cellular oxidative damages. C) Relative immunoreactivity was analyzed in a diagram form following the confocal analysis above, with data expressed as fold changes versus normal control. Scale bar = 20 μm. n = 5 per group. Values are means ± SE. *p < 0.05 versus normal control; #p < 0.05 versus STZ group.