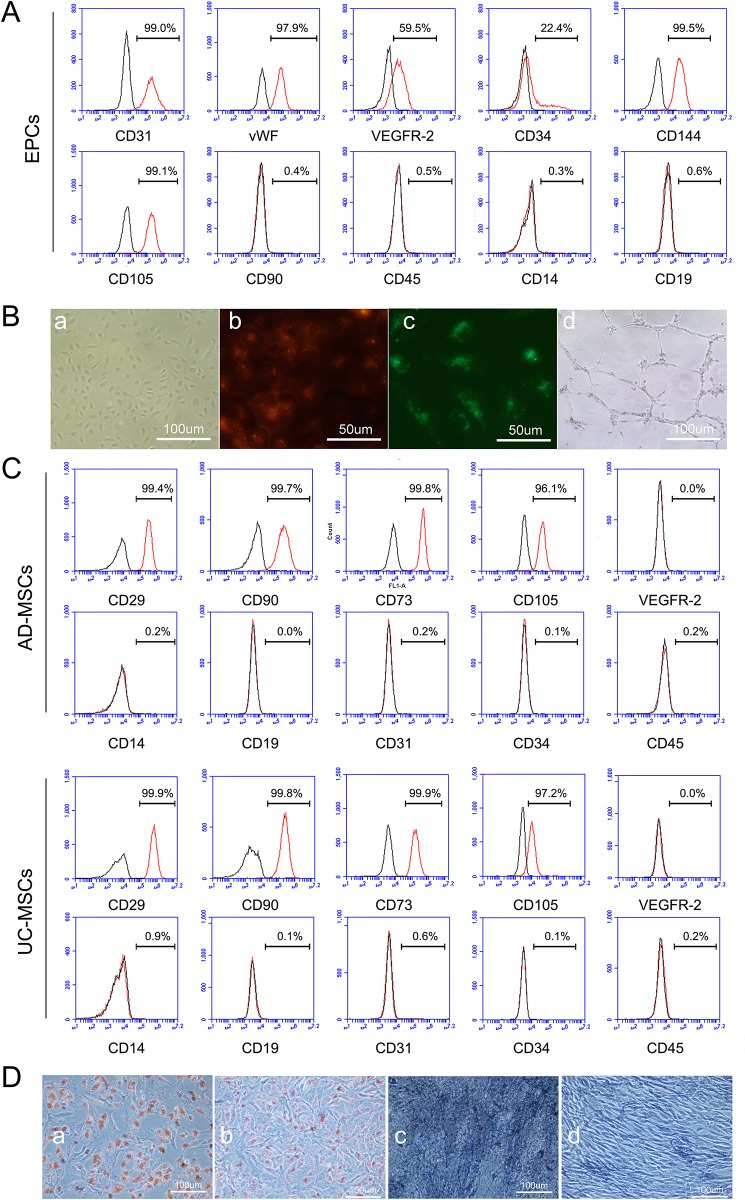
Fig 1. Characterization of EPCs, AD-MSCs and UC-MSCs.
A, Expression patterns of endothelial makers on EPCs were analyzed by FACS. EPCs highly expressed CD31, vWF, CD144 and CD105, partly positive expressed VEGFR-2 and CD34, negative for CD90, CD45, CD14 and CD19. B, Biological function of EPCs was identified. a, Representative phase contrast images of cobblestone-like EPCs. b, EPCs bound with UEA-1 (red). c, EPCs incorporated DiI-Ac-LDL (green). d, EPCs formed vascular-like tubes on matrigel. C, Phenotype analysis of AD-MSCs and UC-MSCs by FACS. Both AD-MSCs and UC-MSCs were positive for CD29, CD90, CD73 and CD105, negative for VEGFR-2, CD14, CD31, CD34 and CD45. D, After 14 days of induction, AD-MSCs and UC-MSCs were differentiated into adipocytes and osteocytes. a, Adipogenic induction of AD-MSCs. b, Adipogenic induction of UC-MSCs. c, Osteogenic induction of AD-MSCs. d, Osteogenic induction of UC-MSCs. Adipogenesis was detected by the formation of neutral lipid vacuoles stainable with oil red O (red-orange). Osteogenesis was demonstrated by detection of alkaline phosphatase activity (brown).