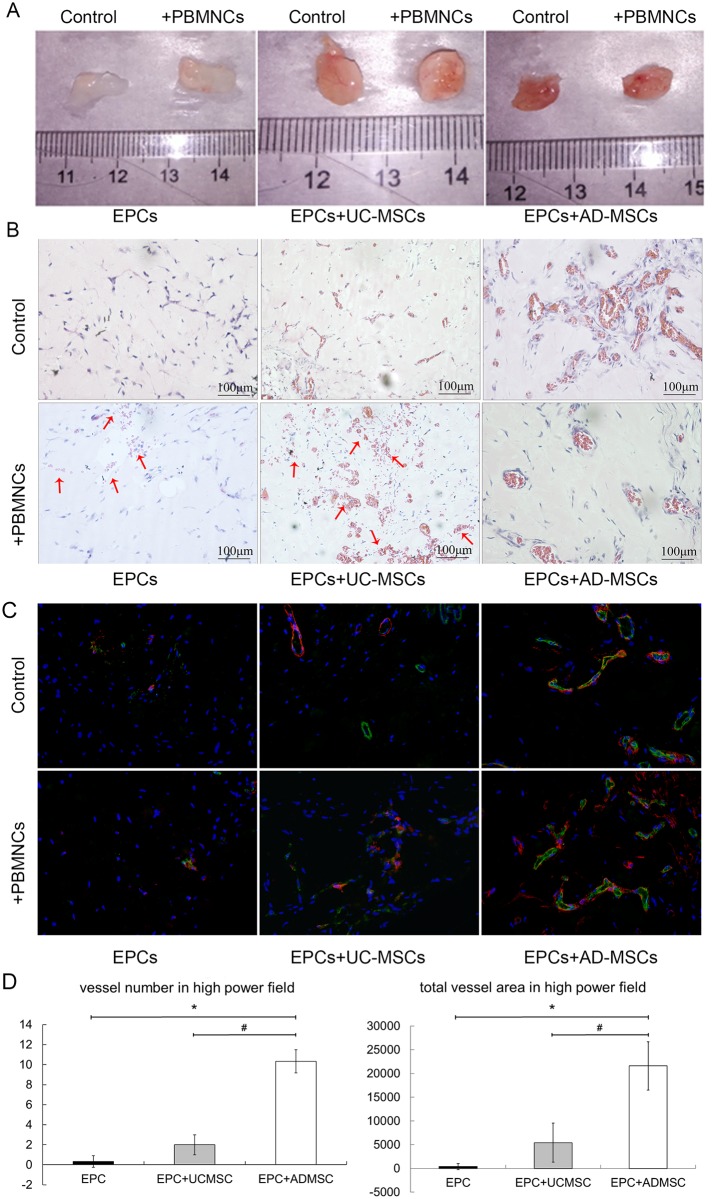
Fig 5. AD-MSCs can promote vessel formation in vivo.
After EPCs were implanted with/without UC-MSCs or AD-MSCs into SCID mice for 2 weeks, formed vessels in matrigel were subjected to immune-rejection by allo-PBMCs. The results were demonstrated by gross observation of the matrigel grafts (A) or by pathological section observation after H&E staining (B) or immunofluorescence staining (green: CD31; red: SMAα; blue: DAPI. 400×)(C). Implanted cells in matrigel formed vessels that inosculated with host vasculature and were perfused with mouse blood. EPCs implanted with AD-MSCs formed more vessels than EPCs implanted alone or EPCs implanted with UC-MSCs (D). The vessels in EPC+AD-MSC grafts also had significantly larger lumen than other groups (D). After allo-PBMC injection, red blood cell leakage was very obvious in EPC grafts or EPC+UC-MSC grafts (indicated by red arrows). In EPC+AD-MSC grafts, the vessels remained stable, and the red blood cell infiltration could hardly be observed.