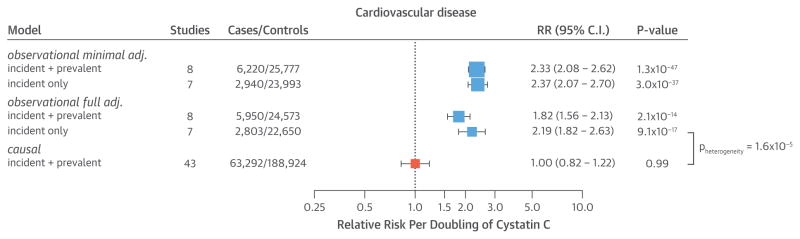
FIGURE 2. Estimates of the Association of Circulating Cystatin C With CVD Risk.
The observational models were minimally adjusted for age and sex (minimal), or fully adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, smoking, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and systolic blood pressure (full). The causal estimates were triangulated using effect estimates of the association of the genetic instrument with cystatin C concentrations (reported in Online Figure 4) and cardiovascular disease (CVD) (Online Figure 12). Total sample sizes may differ from those reported in Table 1 due to the availability of covariates. adj. = adjusted; CI = confidence interval; RR = relative risk.