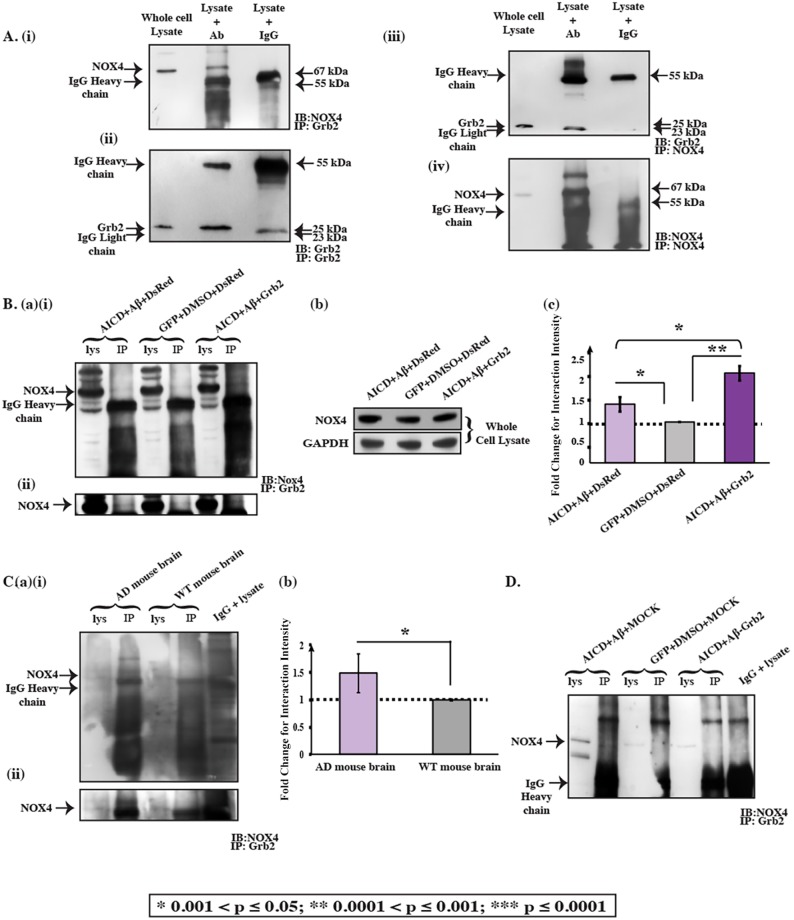
Fig. 5.
The Grb2 and NOX4 interaction prevents cytoskeletal degradation by decreasing the availability of NOX4. (A) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) blot where immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed for Grb2, and then precipitates were immunoblotted (IB) with an anti-NOX4 antibody (i) and anti-Grb2 antibody (ii). Reverse Co-IP blot where immunoprecipitation was performed for NOX4, and then precipitates were probed with anti-Grb2 antibody (iii) and anti-NOX4 antibody (iv). (Ba) (i) The variation of the interaction of Grb2 and NOX4 under AD-inducing (AICD, Aβ and DsRed) and reversal (AICD, Aβ and Grb2) conditions compared to the controls (GFP, DMSO and DsRed). (ii) Higher exposure of the NOX4 bands from the same blot shown in (i). (Bb) Changes of NOX4 and GAPDH under AD-inducing and reversal conditions for whole cell lysate. (Bc) Graphical representation of the intensity of the interaction between NOX4 and Grb2, presented as fold changes relative to control (set as 1). (Ca) (i) Variation of the interaction between Grb2 and NOX4 in AD whole mouse brain lysate compared to WT control whole mouse brain lysate. (ii) A higher exposure of the NOX4 bands from the same blot shown in (i). (Cb) Graphical representation of the intensity of the interaction between NOX4 and Grb2, shown as the fold change relative to WT brain (set as 1). A greater interaction was seen under the AD condition compared to under the WT condition. (D) The interaction of NOX4 and Grb2 under Grb2 knock down. The Co-IP experiment shows that the NOX4 and Grb2 interaction decreases compared to under the AD-like situation, in which both AICD and Aβ were present in abundance. Lys, whole lysate.