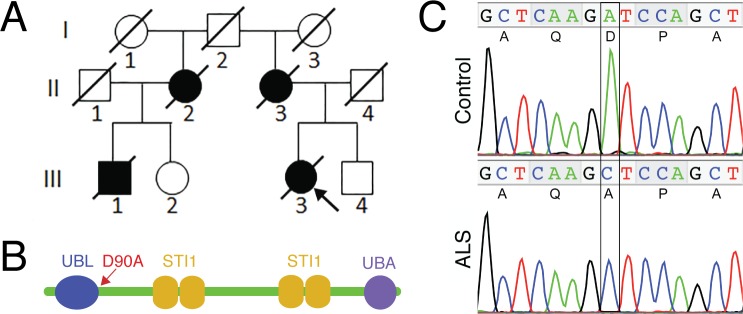
Figure 1. The UBQLN4 c.269A>C (p.D90A) variant identified in a familial ALS case.
(A) Pedigree of a family with ALS. The proband (III3, arrow) had disease onset at 55 years of age, with disease duration of 22 months. Her mother (II3) died of ALS at 62 years of age without clear information regarding disease onset. Her maternal grandfather (I2) died in a traffic accident without any known neurological problems. Her maternal aunt (II2) developed ALS with disease onset at 51 years of age, and disease duration of 36 months. Her cousin (III1) developed ALS at 56 years of age and died five years later. (B) Predicted structural and functional domains of UBQLN4 with an arrow indicating the position of the mutation site. Domains include a UBL: ubiquitin-like domain, aa 13–83; four STI1 heat-shock-chaperonin-binding motifs, aa 192–229, 230–261, 393–440 and 444–476; and a UBA: ubiquitin-associated domain, aa 558–597. (C) Sequencing chromatograms of UBQLN4 wild-type allele in control and mutant allele in the patient with ALS. An adenine to cytosine substitution is present in the ALS patient, resulting in the change from aspartate to alanine at the ninetieth amino acid, D90A.