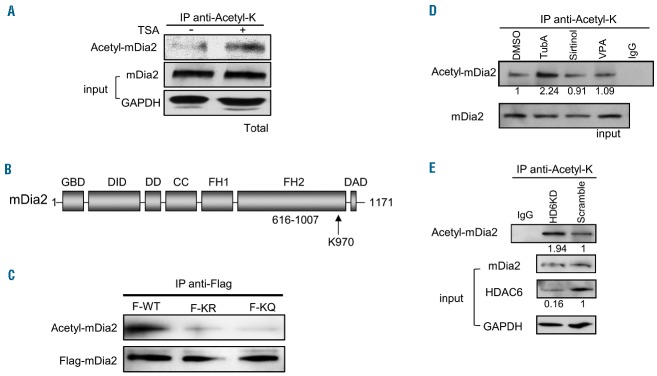
Figure 5.
mDia2 is acetylated in vivo and HDAC6 is responsible for deacetylation of mDia2. (A) Total acetylated protein was immunoprecipitated by anti-acetyl-K antibody from the cell extracts treated with or without TSA in Ter119-negative mouse fetal progenitors. mDia2 protein was detected by specific anti-mDia2 antibody using western blotting. (B) Schematic representation of mDia2 protein structure. K970 is the acetylation site in the FH2 domain of mDia2. (C) 293T cells were transfected with Flag-tagged mDia2 WT (F-WT), mDia2 K970R (F-KR), or mDia2 K970Q (F-KQ). The cell extracts were incubated with anti-Flag antibody and acetylated mDia2 and total Flag-tagged mDia2 were detected by anti-acetyl-lysine (anti-acetyl-K) and anti-Flag antibodies. (D) Total acetylated protein was immunoprecipitated by anti-acetyl-K antibody from the cell extracts treated with or without inhibitors in MEL cells as indicated. Acetylated mDia2 protein was detected by anti-mDia2 antibody. The numbers indicate the relative density of the bands. (E) Total acetylated protein was immunoprecipitated by anti-acetyl-K antibody from the cell extracts of stable HDAC6 knockdown (KD) or scramble control MEL cells. mDia2 protein was detected by anti-mDia2 antibody. The numbers indicate the relative density of the bands. Each experiment was repeated three times.