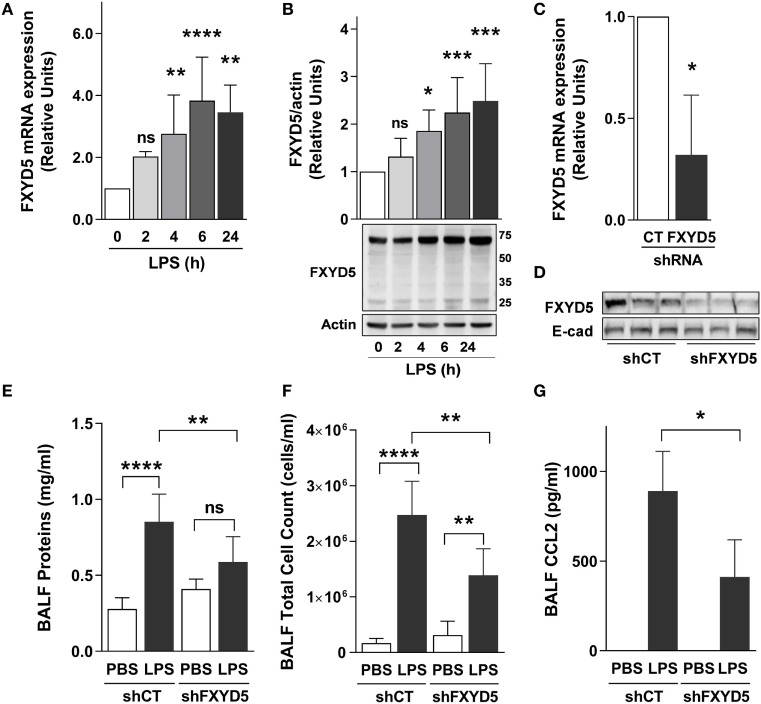
Figure 3.
Increased levels of FXYD5 are required for LPS-induced lung inflammation. (A) LPS was instilled to mice for the indicated times and the levels of FXYD5 mRNA were determined by RT-qPCR in lung peripheral tissue (n = 8). (B) Mice were treated as in A and FXYD5 was determined in lung peripheral tissue cell lysates by Western blot. Bars indicate densitometric quantification of plasma membrane FXYD5 (top band) in relation to actin (n = 8). (C,D) Control (CT) or shFXYD5 lentiviral constructs were instilled into mice. Silencing was assessed by measuring FXYD5 mRNA by RT-qPCR (C). n = 4 or protein abundance in lung peripheral tissue total membranes (D). Representative immunoblot showing the abundance of FXYD5, E-cadherin was used as a loading control n = 6. (E–G) Mice treated as in C were given LPS for 6 h and BALF was obtained. Proteins (E), total cells (F), and CCL2 (G) were determined as described in Section “Materials and Methods.” Values of PBS-treated controls were normalized to 1. Bars represent means ± SD. Statistical significance was analyzed by one way ANOVA and Dunnetts’s (A,B) unpaired Student’s t-test (D) or Sidak’s multiple comparison test (E,F). *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001.