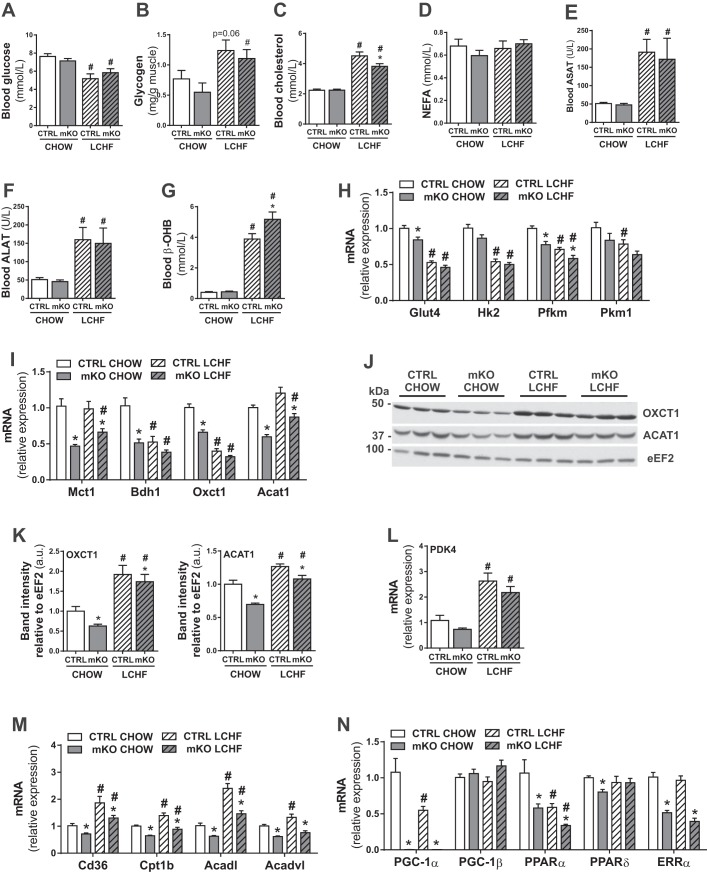
Fig. 2.
LCHF diet-fed mice show a PGC-1α-dependent switch from glucose to fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle. A: plasma glucose levels of mice fed a chow or LCHF diet for 12 wk (n = 7–8). B: relative glycogen levels in gastrocnemius muscle of mice fed a chow or LCHF diet for 12 wk (n = 6–8). C–G: plasma total cholesterol (C), nonesterified fatty acids (NEFA; D), ASAT (E), ALAT (F), and β-hydroxybutyrate (β-OHB; G) levels of mice fed a chow or LCHF diet for 12 wk (n = 7–9). H and I: gene expression in gastrocnemius muscle relative to 18S of genes involved in glucose metabolism (H) and ketolysis (I; n = 6–8). Hk2, HKII. J and K: representative immunoblots (J) and protein levels (K) of OXCT1 and ACAT1 in gastrocnemius muscle relative to eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF2; n = 6). L–N: gene expression in gastrocnemius muscle relative to 18S of PDK4 (L) and genes involved in fatty acid uptake and oxidation (M) and transcriptional regulation (N; n = 6–8). Error bars represent SE. *Significant differences between genotypes: chow-fed CTRL and mKO mice and LCHF diet-fed CTRL and mKO mice (P < 0.05), respectively; #significant differences between conditions: chow and LCHF diet-fed CTRL and chow and LCHF diet-fed mKO mice (P < 0.05), respectively.