Fig. 6.
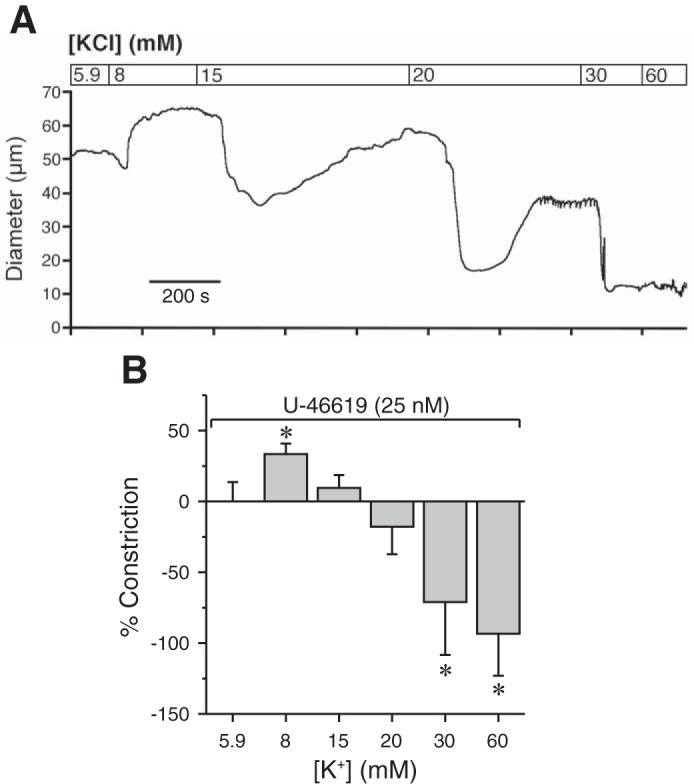
KIR channel activation or inhibition affects bladder arteriole diameter. A: representative tracing of bladder feed arteriole responses to increasing concentrations of K+. Vessels were first constricted with a submaximal concentration of U-46619 (25 nM). B: small increases in extracellular K+ caused relaxation that became constriction as concentration increased, indicative of KIR-mediated relaxation. *P < 0.05 vs. U-46619; N = 3.
