Figure EV1. A synthetic viability screening identifies the SIR complex as the major driver of tof1∆ camptothecin hypersensitivity.
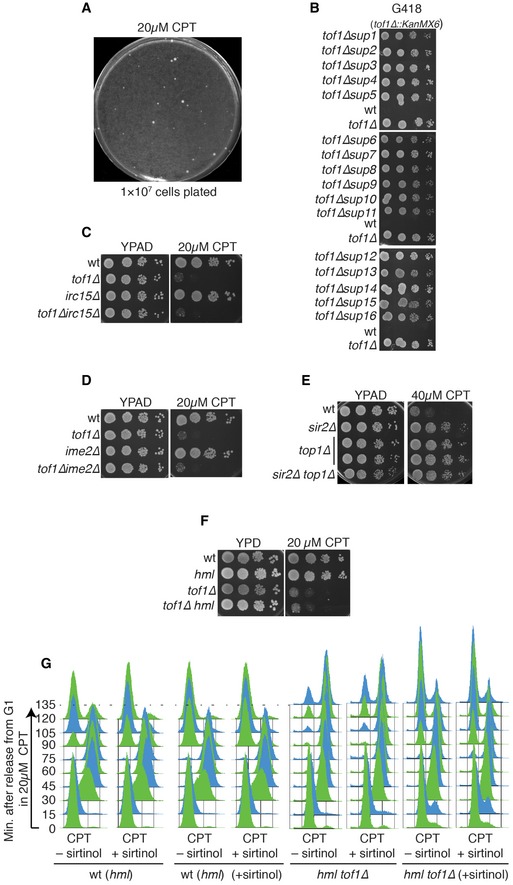
- Spontaneous suppressors of camptothecin sensitivity of tof1∆ cells.
- Suppressor strains recovered from the tof1∆ synthetic viability screen are G418 resistant, suggesting presence of the TOF1 deletion cassette.
- Deletion of IRC15 does not suppress tof1∆ camptothecin hypersensitivity.
- Deletion of IME2 does not suppress tof1∆ camptothecin hypersensitivity.
- Deletion of SIR2 and deletion of TOP1 lead to similar levels of camptothecin resistance, and combining the two mutations does not further increase camptothecin resistance.
- Deletion of HML does not alter the camptothecin hypersensitivity of tof1∆ cells.
- tof1∆ cells and congenic wild‐type cells were pre‐grown either in the absence or in the presence of sirtinol. They were subsequently synchronised in G1 and released into S phase in the presence of camptothecin, either with or without sirtinol. Cell cycle progression was monitored by FACS analysis.
